SEO is difficult when you start out and you need to prepare a bulletproof SEO strategy. Basically, you need to learn about SEO, do research, try things out, make mistakes and gather experience all at the same time in an area that takes a long time to show results in the first place.
Honestly, many companies do not have time for this learning curve. What they (and you) are interested in is the best possible result as fast as possible without too many snags along the way.
Therefore, we skipped the learning curve and made this step-by-step manual to create an SEO strategy – or plan if you’d like – so you know exactly what to do and in which order. It describes the process that an SEO agency goes through with each new SEO client and how they plan the strategy to follow.
Follow this recipe for creating an SEO strategy and you are bound to get results and reap the benefits.
Set up
The first step of the journey is gearing up. This step will make sure that you are ready to dive into each new task without delay and you won’t get distracted or waste valuable time on setting up your analytics, tools or else.
1. Make an SEO schedule

Let’s be honest. Saying “I’ll do this whenever I have a bit of time” will mean you will probably start, but won’t be as consistent or as dedicated as SEO requires, pushing it down a priority list of tasks you do on a daily basis.
And this just adds extra time to the project or, even worse, sets it up for failure right from the start.
So, take some time to make a plan for your SEO as the first thing you do.
This is way more important than you probably imagine but take it from me that have done this for 7 years and have worked with a lot of companies that wanted to execute the SEO themself with only me as a sideline consultant.
✅ 1.1 Put in a couple of hours for SEO twice per week in your calendar
An added benefit of making an SEO schedule is that it puts a limit on how many hours you use and will prevent using too much time and getting lost in a single task.
To start with, you can just make general entries marked as SEO in your calendar and when you are done with all the initial work of setting up and doing keyword research you can be more detailed and set up individual tasks as you see fit.
The dedicated SEO time set up in your calendar will make a difference and help you keep on track while also allowing you to expand your SEO knowledge slowly, but regularly.
A nice way to organize the individual tasks is to use a Trello board or another project management system of choice.
2. Sort out your SEO toolbox
There are plenty of SEO tools and software you can use to be more efficient and get insight from your data. Many of these tools do not come cheap and are only really necessary for professionals and others that deal with SEO on a more regular basis.
Morningscore is prices way under the most known SEO tools to fit all the DIY SEO people like yourself.
The following tools are in my view more than enough to get you started on your SEO journey and successfully execute your SEO strategy.
✅ 2.1 Set up Google Analytics (or other tracking tool)
Google analytics lets you track exactly what happens with customers, where they come from and how they interact with your site.
There are many Google Analytics guides online, so we will not touch upon how exactly to set it up here.
It doesn’t have to be Google Analytics. You can use other tools like Plausible instead as we use in Morningscore.
✅ 2.2 Set up Google Search Console
With the same gmail account you used for Google analytics, set up a Google Search Console account and connect to your website.
✅ 2.3 Set up your domain in Morningscore
Add your domain to Morningscore. It’s important to do this as early as possible so our Spaceman has time to fetch all your data.
✅ 2.4 Set up a system for documentation
It would be smart to keep a log with every change you make and each link you build. This way if you see big jumps or dips in your ranks or link rank you will be able to figure out if it has anything to do with the changes you’ve made.
Alternatively, if this log system is just not something you will keep updated – Morningscore keeps a history of links and improvements.
3. Find competitors
✅ 3.1 Make a list of your competitors
Make a list of your biggest competitors is an important part of the early stages of the SEO strategy. These can be local companies – the ones you know are directly competing with you or for your clients if you are at an agency. Or they can be big national companies that you look up to and want to copy a bit.
Keep in mind though that these large companies will be difficult to overtake on ranks as they probably invest more money into SEO than you do. The key is not find less broad keywords to rank for that the big players haven’t shown too much interest for.
✅ 3.2 Add your competitors to Morningscore
By adding them to Morningscore you will get access to all their keywords, rankings, and links.
4. Make a landing page priority list
It would not make sense to optimize every page on your website as it is time consuming and probably wouldn’t make much of a difference.
This is especially true for very large websites.
This is why you need a priority list to know exactly what you should focus on and to make sure that important pages get enough attention.
✅ 4.1 Make an initial landing page priority list
Make a list of pages that you think are the most important. These are usually the front page plus any page that showcases the product or service you are selling or those that are informative/important for your target group.
Often, if you have a webshop, these pages are your product categories.
✅ 4.2 Download a performance report from Google search console
In Google search console, under performance, make sure that the date range is set to at least the last 3 months and then export the data in a file of your choosing.
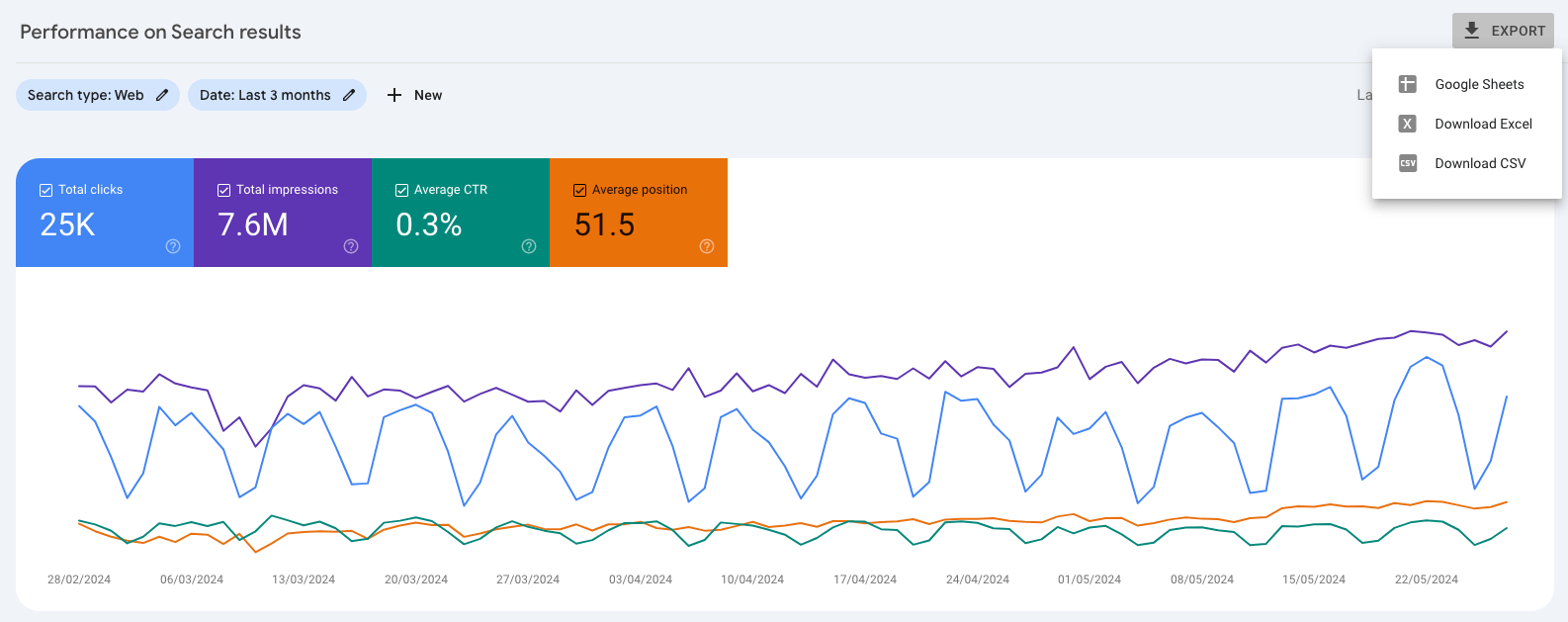
In the file, choose the pages tab and it should give you a list of all your websites pages with the number of clicks, impressions, average CTR, and average rank.
Sort first by impressions (largest to smallest) and delete all but 20 pages (or more if you believe that you have more really important pages or have more time for the upcoming SEO work).
Add the pages from your initial priority list if they are missing here and remove those that you feel are not relevant.
Next, sort by position (smallest to largest) and you have a list of pages on your site that are shown in SERPs the most and that rank the highest.
Depending on the niche you are in and the state of your website – It usually makes sense to find the best performing pages and then give them a little nudge and make them do even better than optimizing an old page that isn’t ranking at all.
Go through the first 5-10 pages and see if they make sense to optimize (Are these the pages that could potentially bring you in more clients? Or do they bring in large amounts of traffic that you can benefit from?).
If the answer is yes, you have your landing page optimization priority list sorted.
5. Set up performance measuring

✅ 5.1 Make a list of KPIs
Usually when we talk about SEO it’s the ranks we are after, right? But the KPIs also depend on who your users are.
If you are interested in traffic, then that is what you should be tracking. And if you are interested in users with buyer’s intent then conversions make more sense.
You will need Morningscore and Google analytics (or other tracking tool like Plausible) to track these KPIs, all depending on which KPIs you choose of course.
✅ 5.2 Set up missions in Morningscore
Morningscore missions come in 3 categories based on what they track – keyword rank, links and health/onpage.
You can either choose the missions that Morningscore suggests automatically or you can make your own by adding new ones.
Keyword strategy/plan
6. Keyword research
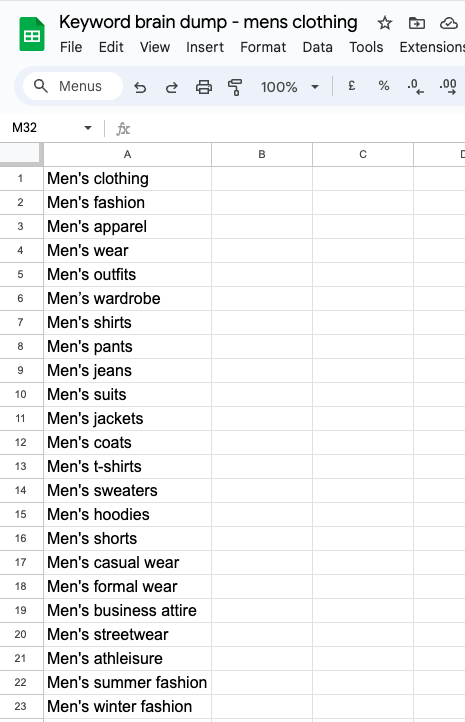
✅ 6.1 Do a keyword brain dump
Open an excel file and start writing whatever keyword comes to mind when you think of your website, business, product, and service.
Start with those that you think best fit your business, product and/or service. Example below from keywords related to a mens clothing business (short example – you want a way, way longer list).
It’s important to be a bit critical here and really make it clear what you are selling – it’s not about getting more traffic (in most cases), it’s about getting the right traffic.
Put yourself in your client’s shoes. We all find products and services on Google, so replicate that from your client’s position.
What would you type in the search bar if you wanted to buy your product or service? Or even better, ask your customers! Which search terms did they type in to find you?
✅ 6.2 Scrape the keywords your competitors use
To get your competitor’s keywords you can either go through their website manually and write down the words that they continually use or you can use Morningscore.
If you add your competitors to Morningscore you will be able to see all the keywords they rank on. You can then export the full keyword data for each competitor.
Open a new excel file (or make a new tab in the keyword file you worked on from the start) called Competitor keywords and copy the data from all the competitor files into the same place.
Next, delete everything that has a low search volume (what low search volume is depends on the size of your niche – for some it can be anything under 100, for a small business with a specific language/country it could be as low as 20 or 10).
Remember: Use common sense. A keyword with 0 search volume doesn’t necessarily means 0 as no tool can show you that exact data. These keywords can have potential.
Now there are two tactics you could use, depending on how much time you want to use on this step.
The slow, but detailed tactic:
Use the “Remove duplicates” feature and then sort alphabetically. Go through the entire list and remove any keyword that doesn’t seem relevant to your business, product or service.
The shortcut tactic:
Sort alphabetically and keep only the keywords that appear multiple times (meaning almost all of your competitors use them).
This tactic saves you a lot of time compared with the first, but you miss finding good keywords that your other competitors might not have thought of and those are easier to rank for because of less competition.
✅ 6.3 Get Google to help you out
You can use Google suggest to find long tail keywords. Pick a keyword with a ton of search volume and then do the ABC method.
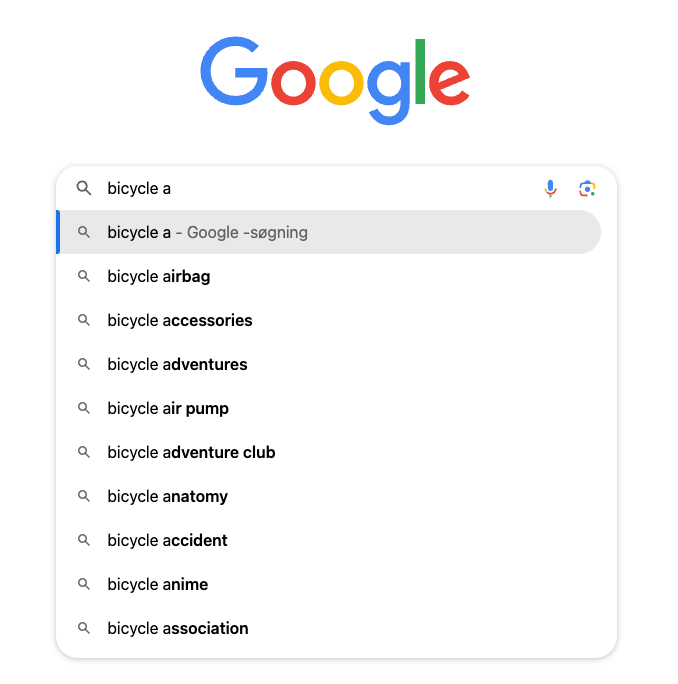
The ABC method is where you take a keyword and copy it into Google’s search and take note of the suggestions in the drop down box.
Then you type space after the keyword followed by “a”. Write down relevant suggestions again. Delete “a” and type “b”. Note down suggestions again.
From there you continue down the alphabet trying to get new longtail keyword ideas.
You can also check the bottom of the SERPs for “Searches related to..” and note down suggestions there.
✅ 6.4 Set up the Morningscore keyword rank tracker
Add your lists from the keyword brain dump (6.1) and Google suggest (6.3) steps to Morningscore’s keyword rank tracker.
Sort the keywords by search volume and delete those with too low search volume.
Feel free to sort them into folders now or mark some of the keywords as your favorite. This will make it easier for you to keep an eye on rank fluctuations and compare to how your competitors are doing.
You can add keywords to folders and group by target landing page, search intent, subject, or whatever structure fits you.
✅ 6.5 Make sure your keywords match the search intent
Morningscore’s keyword rank tracker has a very handy feature that will help you determine search intent. By right clicking on a keyword in the tool you get a small menu where you should click on “See all ranks”.
Now you can see the exact SERPs for the keyword and delete it if you notice that the results are completely different from what you are offering.
To determine the search intent you should look for the words being used and the type of landing page that are ranking.
If all results are product pages the search intent is to buy a product. If you see a lot of blog posts, wikipedia, etc. the intent is to find information about the subject.
✅ 6.6 Use your tracked keywords to find your organic search competitors
While you are checking the keywords for search intent, note down which competitors are ranking on the top 3 positions for keywords that are your favorites (those with the most potential or those that you have decided to use in optimizing your most profitable landing pages with).
You might want to add these competitors to your Competitor list (3.1) and do a bit of additional keyword research using their websites (6.2).
✅ 6.7 Get additional suggestions from Morningscore
If you think your keyword list is still a bit thin and you could use some more inspiration, try out Morningscore’s keyword research tool.
Add your keyword to the keyword research tool one by one and see if any relevant keywords appear.
Use the filters to customize the results by ignoring keywords with low search volume, keywords containing other brand names and other characteristics that makes the keywords irrelevant for you to target.
✅ 6.8 Combine your data
Take your landing page priority list and add to them your tracked keywords. Choose 1 primary keyword for each landing page and 1-5 secondary keywords. You should only use a keyword once and never optimize one or more landing pages for the same keywords.
If a keyword has multiple search intents you can succeed by creating 2 different landing pages targeting each intent.
This list will speed up your onsite optimization process.
Export your keyword details in Morningscore and check if a keyword is already ranking on google and use the same landing page to further optimize.
✅ 6.9 Make a “Future content” list
There might be keywords that seem really promising, but you don’t really have a landing page that you can use them on. Keep these keywords for content you will make in the future. (This list will come handy in step 8.1).
Content strategy/plan
7. Content optimization
It’s time to get your landing page priority list (keywords included) and start optimizing these landing pages one by one. Pick a landing page and go through steps 7.1 to 7.6.
✅ 7.1 Check your URLs

It’s important for your URLs that they are user friendly. What I mean by user friendly is that they should be readable and easily memorable. With an optimized URL, your users will know what to expect right away and will be more likely to click the link.
Instead of having a URL that looks like this: https://www.example.com/blogarticle.aspx?ID=11526&IT=5f7d3d your URLs should contain keywords.
So if you are a SEO specialist and want to optimize your blog article for the keyword “SEO strategy”, then that is the best to use for your URL: https://www.seospecialist.com/blog/seo-strategy . Use your keywords and hyphens “-” (not underscores “_”) to separate words. Underscore is not a valid space separator for Google.
Do not use your entire blog article title either, try to sum it up instead.
Don’t overdo it either. Stuffing as many keywords in as possible will not do you any good: https://www.sportshop.com/shop/57-sweatshirt—hoodies-sweatshirts—kids/926-sweatshirts—sweatshirt-for-kids/
The URL should be as short as possible (memorable, remember?).
Always keep this in mind when making new pages and have a good search engine optimized URL from the start.
If you are changing the URL of a landing page that has been in use for a while now (and you have internal links and are getting backlinks for it), you shouldn’t forget a 301 redirect. This is crucial if you want to keep the existing ranks and link value of the landing page.
Creating a new landing page without setting up 301 redirects will make Google see your new landing page as a new separate landing page and not a replacement for the old one.
✅ 7.2 Optimize the title tag

The title tag is the clickable headline of your listing in the SERPs. It is important for both CTR and SEO that you include the keyword here. It’s also best, if the keyword is placed as close to the start of the title tag as possible.
The title tag can be too long and if yours is, Google will cut it off and replace a part of your title tag with “…”. This way you could have important words omitted, so keep your title tags between 55 and 70 characters long.
Check the landing page in Morningscores SEO checker, you will get the warning if the title tag is too long (or too short).
✅ 7.3 Optimize meta description

The meta description is the text displayed right under the title tag in the SERPs. This text does not play a big role for SEO, but it does have an effect on CTR. So make sure to write it as appealing as possible and include the keyword to get more users to click on your listing – which in the end can affect your SEO.
Keep the meta description under 160 characters, so you don’t risk Google cutting it and vomiting important information. Or even worse, Google could pick random content to display as your description if the page content doesn’t match your description.
✅ 7.4 Optimize your H tags

As a rule, always include the main, primary keyword in your <H1> tag and use the H1 tag only once. If your landing page has only one <H2> and one <H3> tag, I would be careful of using the primary keyword in all of them – and only use them if it makes sense for the content that follows but it should be relevant as you create content for that exact subject.
If your page has multiple <H2>, <H3> and even <H4> tags then you can be more liberal with using the main keyword in one of each and then use the secondary keywords in the rest.
A rule of thumb is to use your keywords in about 70% of your H-tags and always in your H1.
H tags are meant for marking content hierarchy, not for setting font size. Think of it as reading an important text and using a highlighter to mark what is most important. Mark the content with H tags from h2 to H6 appropriately and do not skip tags – so don’t use H5 if you are not using an H4 anywhere on the page.
If the only tag your landing page is using is H1 you should consider adding at least the H2 and H3 (Morningscore will report not having H2 or H3 tags as an issue).
Why is this an issue? Firstly, readability. If you have a big piece of text that is not broken up, it will be hard for the user to read and search engines will not rank it properly.
Look at this very post and see the heading structure and also the line breaks which I use often to increase readability and headers to mark the hierarchy.
✅ 7.5 Add the keyword to the first content paragraph

Ideally, your primary keyword should be popping up naturally through the entire content of your landing page. Naturally means that it follows the content and you are not just trying to shove it in just for the sake of it.
This will happen automatically if you focus on covering the whole subject around your keyword. You need your keyword to create content around it, so don’t force it in where it doesn’t belong.
It is however good SEO practice that it appears as soon in the content (under the <H1> tag) as possible. This is usually the first block of text within the <p> tags or within the first 100 words.
✅ 7.6 Add semantic/related words to your content

You can’t keep using your keyword over and over, but you still need to be very clear on your subject to serve quality content that is original, helpful and adequate.
By using semantically related keywords in your content you help Google understand the context and the subject in general as Google is well aware of words, their meaning and what they are related to.
This will at the same time make you cover more areas in your content that users might find interesting.
✅ 7.7 Add internal links

Internal links is an important and often underrated SEO factor. Internal links are guiding users around your website as well as search engine crawlers.
Make sure to link to relevant and important pages to boost them. Do not overdo it so choose the most relevant ones.
Link with the anchor of the keyword the landing page you link to is optimized to rank for and never the keyword that the linking page is optimized to rank for.
Following the checklist above will give you a well optimized page that looks something like this:

✅ 7.8 Check if the content of your landing pages needs to be expanded
Use Morningscore’s keyword rank tracker and click on the keyword you are using to optimize the landing page. Click on “See all ranks” in the menu that appears. This will bring up the SERPs for this keyword.
Open the first 3-5 results and check their content. How does your content match up to the top performing websites? Can you expand your content to make your landing page better? Can you write something better than what the top websites have? Add this content expansion to the Future content list.
The idea here isn’t to rephrase what they are already saying. You need to figure out how to make sure to cover what they do and additional helpful information.
✅ 7.9 Onpage SEO checklist
Onpage optimizations is a big deal and is very important to rank on your selected keywords. To do so, make sure that you have done a good job with all of the points above. Her is additional elements to optimize:
✓ Use short, precise and meaningful URLs and use hyphens as separator
✓ Add your keyword first in the page title, add call-to-action and keep it under 70 characters
✓ Write appealing meta descriptions that makes users interested in your page and keep it under 160 characters
✓ Always add your main keyword in the H1
✓ Make sure that your main keyword is in around 70-80% of your H2’s
✓ Include semantic (related) keywords to add context and help search engines understand your content
✓ Add internal link to boost other important pages
✓ Add your keyword within the first 100 words (above the fold)
✓ Make sure to have 1.000 words in your content targeted the subject (or even 2.000 words for blog posts)
✓ Check grammar. Grammar is a ranking factor so make sure to double-check or use tools to help you with correct grammar.
✓ Use keyword variation for image alt-tags
✓ Rename image-files to have relevant names
✓ Compress images using tinypng or other tools
✓ Use awesome images and videos to increase time spent on page
✓ Write engaging content that keep users reading – be original and helpful
✓ Add outbound links to relevant and authoritative pages
✓ Optimize for conversions. Don’t make the user think, make it easy to convert and show the way
✓ Use a good cache-service
Read our comprehensive SEO checklist, which includes off-page, technical, LLMO and more.
8. Finding new content opportunities
✅ 8.1 Pinpoint missing content
Remember the Future content list from step 6.9? Time to make use of it.
Copy the keyword list over into an excel sheet (or Google sheet) and for each keyword plan out what kind of page would be most appropriate. Is it a landing page explaining a service? Maybe a blog post talking about a product that you are selling? Or a case study?
Do a Google search for the keyword you are planning for and look through the pages that pop up in the first 5 results. What kind of content is it? Can you make something that is better and more informative?
If all results are product pages it seems that Google has found out that the search intent is to buy something. If all results are blog posts it’s more likely to be informational searches – and whatever the intent is, you need to match it to be able to rank.
Google will never show a product page for an information search and will never show an informative blog post when a user searches for “buy Nike trainers”.
✅ 8.2 Check out the competition
Do a detailed analysis of your competition. Take a competitor from the list you’ve made in step 3.1 and go to their page.
Read through each of their pages thoroughly (well at least those that seem relevant to you) and note down any content you might feel your website is missing. This can be either a whole page or small pieces of content that could improve your existing landing pages.
✅ 8.3 Make a detailed content plan for the next 6 months
A detailed content plan will help you stay consistent and structured and can save time rummaging through multiple files.
Write if it’s a new landing page, blog article or a content expansion of an existing page. Note down the URL (existing or a proposition for a new one), the keyword, who is writing it, the deadline, how long it should be (how many words?) and any other important information (like where did you get inspiration from – a competitor?).
You can even choose to create a content brief or add content outlines if you already have an idea of what content the page is supposed to cover.
A bit about the deadline.Small additions to already existing landing pages should be done as soon as possible as they will help you rank.
New landing pages are second priority and how soon they need to be up depends on your business. If it’s a new product or service that is not in sale yet, then the page needs to be ready a few weeks before the product is.
If the new landing page uses a keyword with a big potential in getting you conversion, then it should be done sooner rather than later.
And lastly blog articles (if you have a blog) should be done regularly and continually. Depending on your resources anything from once per month to 2 per week is fine.
And how do you know how long the content should be?
This depends purely on what type the content is. Usually it’s the more, the merrier, but it can be difficult to reach more than 200 words for a (let’s say) contact page that only has the address, phone number and email.
As a rule of thumb, ideally blog articles are between 800-1500 words. Your landing pages describing products and services should follow the same rule with an absolute minimum of 300 words.
Often, you need quite a lot more content on your category pages as well. Check your competitors’ pages and aim to have more content than the top 3 ranking websites.
Technical strategy
9. Technical SEO
If you don’t feel at home with doing detective work in your code and you are not an “Inspect” native, you should probably use a tool that will help you keep track of all the SEO issues.
Morningscore gives you a good overview of the health of your website both in general and landing page view.
9.1 Global website issues
Use the health tool in Morningscore and check the Technical factors in General performance. If Morningscore is reporting any of the following issues – fix them. If not, feel free to skip to step 9.2.
We call these issues global because they are not bound to a specific landing page, but instead affect the whole website. You will only need to fix them once.
✅ 9.1.1 Add schema markup
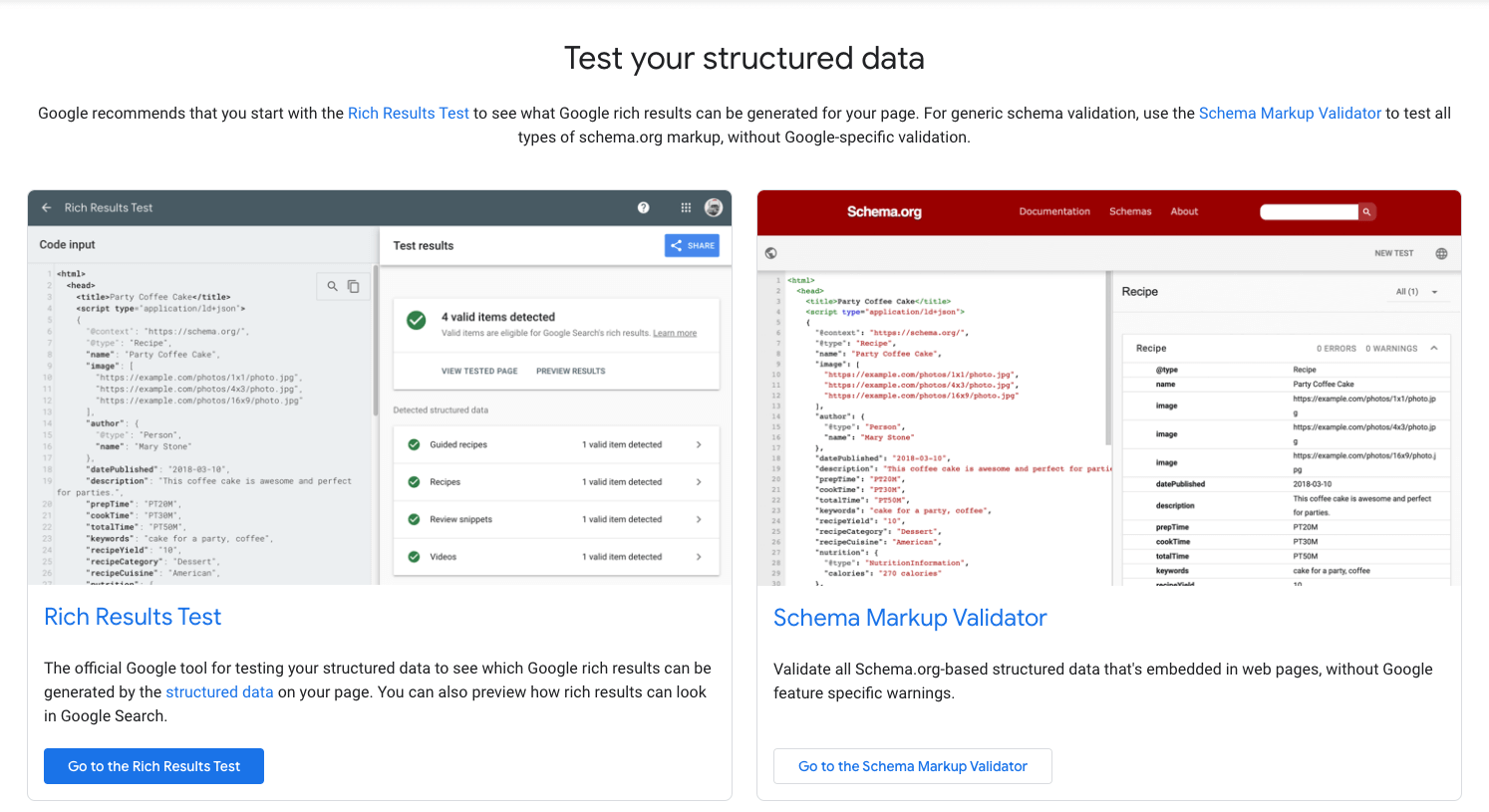
Schema markup is a way of informing the search engine on what your website (or landing page) is about.
The most important type that you should concern yourself with is the “Organization” schema and it should be added inside the <head> tag of your front and About page.
Once you upload it, test the page URL with the Structured Data Testing Tool. If you are unsure of what to write, check out your competitor’s schema by using the same tool and get some inspiration.
There is several types of markups you can use depending on your type of business. You can markup products, prices, stock, opening hours, restaurant menu, courses, and a lot more.
If you are uncomfortable with this (I understand, it can look scary) you can use simple plugins for Wordpress, Shopify, and others as Rank Math so you don’t have to even enter your sites code to add Schema to your pages.
✅ 9.1.2 Check your 404 page
When Morningscore health tool reports that the 404 page is missing, it actually means that the 404 page is not customized.
You can check your website easily by adding /is-my-404-customized right after your domain name (ww.domainname.com/is-my-404-customized). As it is highly unlikely that you have a page with this URL this should trigger a 404 error and you can now see what your page looks like.
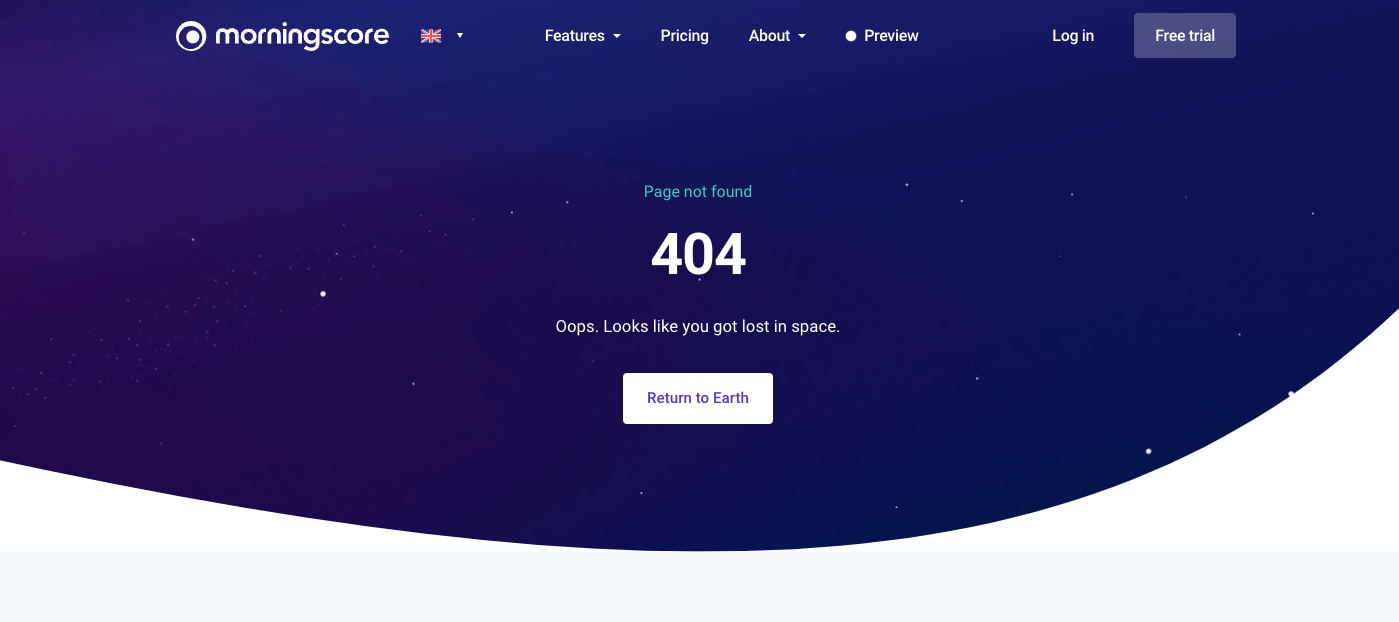
If it looks similar to your website (your website header and footer are included with all the menus, links and info) then you are all good.
If the page looks weird and there are no links back to your site, you will need to make a customized 404 page.
Each page on your website needs to provide a good experience to the user and encourage them to try with some other page on your website and continue browsing. Without a customized 404 page, the user will most likely bounce.
✅ 9.1.3 Sitemap
A sitemap is an XML file that lists all the URLs on your website. By using a sitemap you can inform the search engines about the pages present on your website, any latest updates and the frequency of the updates.
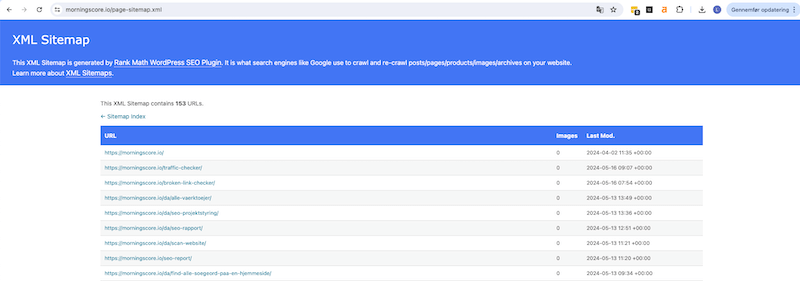
If your website is missing a sitemap the fix is quite easy. There are plenty of online generators like https://www.xml-sitemaps.com/. Just enter your website URL and you will be able to download a XML file.
This file should now be added to your website (preferably with the standard URL path www.yourdomainname.com/sitemap.xml) and it’s location should be added to the robots.txt file.
You will need to keep the sitemap updated and add any new landing pages you create. Alternatively, you can use a plugin that will generate a sitemap automatically and keep it updated for you.
For non-technical users I recommend to use a plugin to handle this. For example you can use Rank Math or Yoast depending on your CMS.
Instead of adding your sitemap location to robots.txt, you can upload your sitemap to Google search console. However, you will need to do this each time you add a new landing page.
✅ 9.1.4 Add a favicon
A favicon is a small image (16×16 pixels) that represents your website and is used in the URL bar, browser tabs, bookmarks and next to your URL in the SERPs when displayed on a mobile. Pages without a favicon will have the default icon (grey globe) displayed.
![]()
The favicon has no impact on SEO, but increases brand awareness and makes it easier for the user to jump back to your page when browsing many websites at the same time (which is typical for the so-called consideration phase in the buying process).
✅ 9.1.5 Check for H tags in the footer
H tags are used to mark up content on your website pages. They are used in order 1-6 and include keywords to make it clear to both users and search engines what the page is about (and which search term you want to rank for).
Using H tags in the footer messes up the structure of your content as they are topically unrelated.
It is also a problem if you use H3 tags in the footer and H4 tags in the content as the search engine won’t understand that the H4 tags in the content are more important for both you and the user.
Change the footer content from H1-6 to <p> or <span>.
Remember, H tags is not for controlling font size but for marking the content hierarchy and optimizing readability.
✅ 9.1.6 Do you have SSL enabled?

SSL is a standard security protocol for establishing an encrypted link between your website and the user’s browser.
You can make sure that your SSL is enabled by typing https:// in front of your website URL in the browser search bar. If you get a warning, your website doesn’t have SSL enabled.
Even if your site doesn’t collect sensitive customer information, search engines suggest that switching to https is a good idea and may help improve rankings.
✅ 9.1.7 Use redirects to your advantage
When you have an old page that you are not using anymore and you want to get it removed from the SERPs there are 2 options.
For pages that have backlinks and a new relevant page, with improved content was made to replace them – you should use a 301 redirect.
This will pass the link equity to the new page and you will be able to keep some of the SEO benefits. This is usually the recommended way of removing a page.
Alternatively, you can set the page status to 410, marking it as deleted permanently. Any existing backlinks will return a 404 error which means that they will probably be removed. So use this option only if the page has no internal or external links.
✅ 9.1.8 Check your About, Privacy, Contact & ToS pages
About, Privacy policy, Contact and Terms of service pages are pages every website is expected to have. This expectation is shared by users and search engines alike as it gives a signal of trustworthiness and increases Page Quality.
Check if you have all these pages (or pages that combine the content – example ToS + privacy policy). If not, you need to make them.
✅ 9.1.9 Optimize crawlability
Depending on the number of your website pages, Google’s search engine will not always crawl your entire website. According to Google, making so many requests to the server would slow down your website significantly, so they use something called a crawl limit or crawl budget.
Because of this it is crucial that you set your website up to get the maximum out of each crawl.
First and foremost – prune your website and remove old, outdated pages that are of no use to you. Don’t forget to set the right status code (301 for redirects and 410 for deletion).
The second thing you can do is to make sure your website has a flat architecture. Basically, following the rule that the user doesn’t have to click more than 3 times to reach any page on your website when starting from the front page.
Third – use internal linking and make sure there are no orphan pages that no other page (on your website) links to. An orphan page is a page that isn’t linked to anywhere on a website.
9.2 Landing page specific issues
Use your landing page priority list and start with that instead of trying to fix every general performance issue that Morningscore health tool reports for your website.
Check each of your priority landing pages in the Morningscore health tool, but also follow through each of these steps to make sure you get everything optimized to its full potential.
✅ 9.2.1 Check the page speed
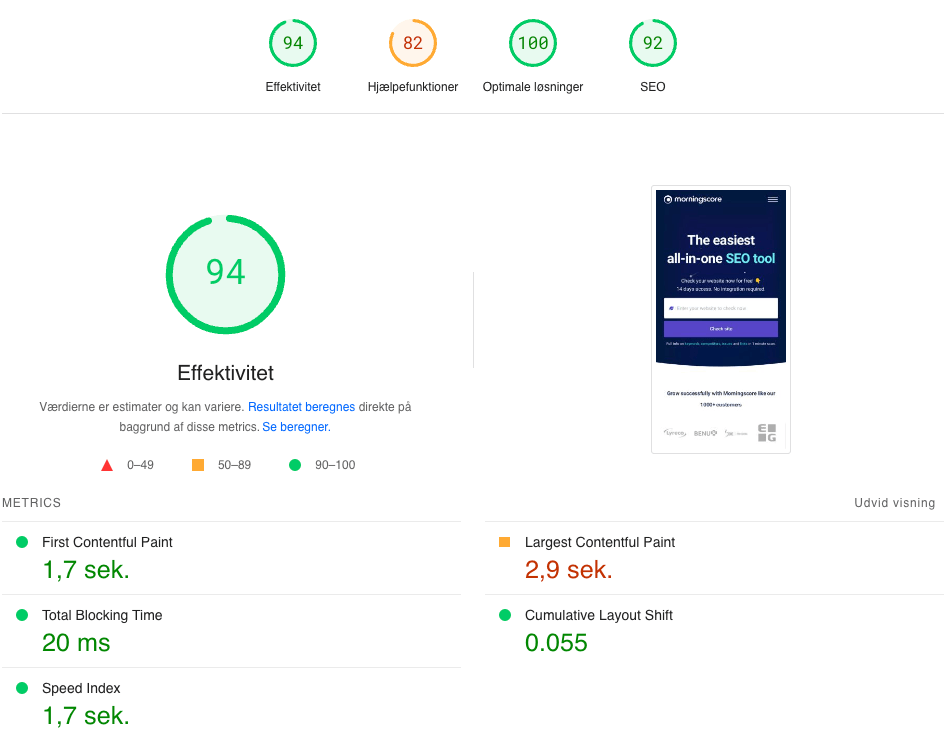
Page load speed is a ranking factor. Search engines favor fast websites and will place them higher when compared to a website that has very similar content but is slower.
You can check your page speed with either PageSpeed Insights or with GTMetrix.
Either will give you a good idea of your website speed and will also give you suggestions on how to fix issues.
Most likely you will need help from a web developer to fix the recommended issues, but what you can do to keep page load down is optimize images (9.2.6) and place them below-the fold and reduce the amount of plugins you use on your site.
✅ 9.2.2 Is your landing page mobile responsive?
Google has been using mobile-first indexing for a while now. What this means is that Google prefers to crawl the mobile version of your website. And you won’t like your results if your website isn’t mobile friendly.
By using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test you will get the most reliable result for obvious reasons.
If your result is green, you can continue down this checklist.
If not, look through the improvement suggestions. You’ll probably need a web developer to help you in fixing the issues.
✅ 9.2.3 Remove duplicate content
You should avoid duplicate content through your website. Search engines want unique, original, and relevant content.
The most commonly duplicated content are the title tags, meta descriptions, H tags and content blocks (text) used on more than one page with minimal variation.
Sure, having a single slider that is shown on all pages isn’t counted as duplicate content and won’t punish your performance. But having several similar content sections can potentially harm your SEO results.
Make sure that all of your content is original and isn’t duplicated from your own pages or other websites content.
✅ 9.2.4 Optimize the H1 tag
Every page should have one and only one H1 tag. This is the most important H tag on your page and it should contain the main keyword, preferably at the beginning.
Check if your H1 tag is missing or if you maybe have more than one in which case you need to change one to H2 (or whichever tag makes more sense in the structure).
✅ 9.2.5 Check for broken links
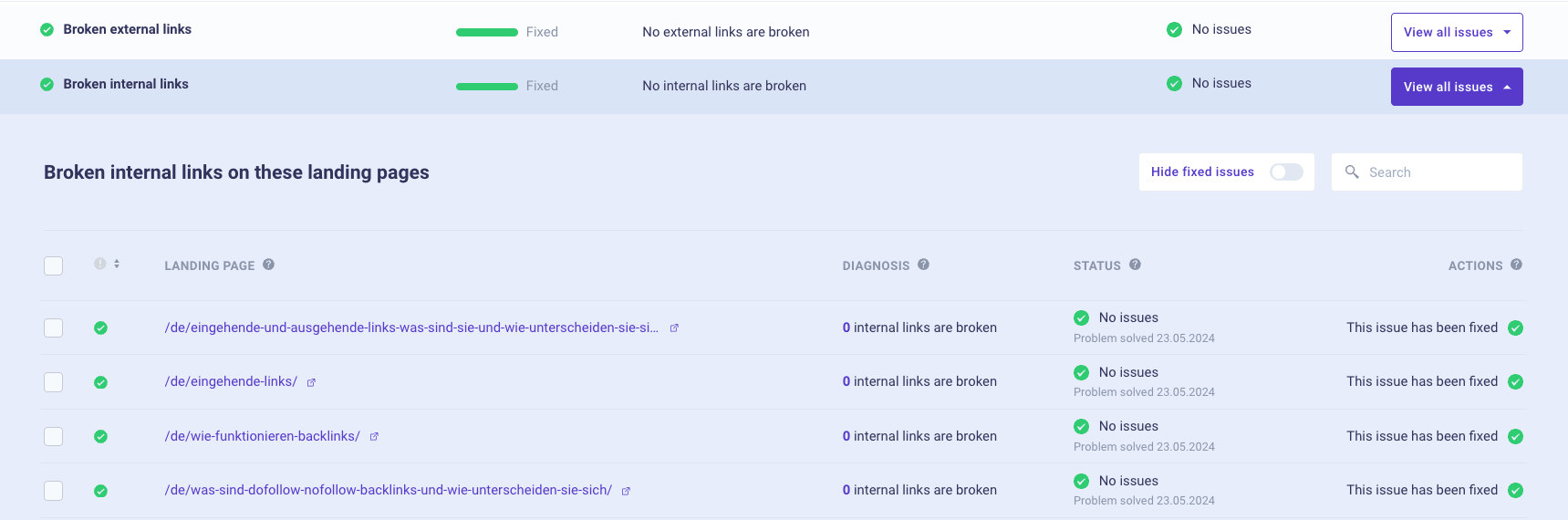
Morningscore’s health tool will give an error if you have a broken internal or external link. This is especially common for landing pages with older content.
For internal links – make sure that the link is correctly written if the page you are linking to still exists and replace it with a link to another internal page if the original page has been removed.
For external links – again, first check if the link is written correctly. If the website you are linking to had the page removed, simply find another relevant source to link to instead.
✅ 9.2.6 Optimize images
Images are important for user experience. They make visual breaks in the content, improve readability and make the content more memorable and understandable.
Usually the larger the page is, the more images it has and this can have a negative effect on page speed and SEO if they are not properly optimized.
There are three things we can optimize when it comes to images:
- Image file name
Image file names are one of those places where you can get a few keywords in without it affecting the content your users can read. It is so often the images have names like img3434937.jpg or image07.jpg and that’s a good opportunity for optimization.Have the image file name tied in to the content that surrounds it. Look at the closest H tag and paragraph and what they are about and name the image something similar, but short. So if you are writing a SEO strategy and you are including an image of a SEO schedule excel sheet then you can name the image seo-strategy-schedule.jpg or seo-schedule.jpg. - Image file size
If you are changing the file name and reuploading images you might as well do some speed optimization while you are at it. The easiest way to do this is to use https://tinypng.com/ and let the panda sort everything out. The resulting images will be smaller, without compromising the image quality. - Alt tag
Most CMS’s will not give you trouble adding alt tags. In most WP themes it’s as simple as adding them to the image in the media library. However, web developers like to make our lives complicated sometimes and not include the code for alt tags or set all the images as backgrounds. There you will need to get a hold of one of these elusive creatures and get them to help you out. Hopefully, this is not your case and you can add them in easily. Alt tags should be descriptive. What google means by this is – describe what’s on the image. But if you just wanted something visually nice and the description has nothing to do with your content then you might have to be a bit creative. There “Man looking at chart” becomes “Man plans SEO strategy”. Please do be mindful of not abusing this though. People often think they can stuff whatever they want in an alt tag because only spiders will ever “see” it. But this is not true, alt tags are used to make website pages accessible for people with disabilities and are read out by voiceover software. This is also a reason to not write gibberish or a string of keywords.
✅ 9.2.7 Be mindful of keywords in the anchor tags
The focus keyword that you are using for a specific landing page should only be used as anchor text somewhere else if it links to that exact landing page.
Example: If you are optimizing your page for the keyword “SEO strategy”, then including an external (or internal) link with the anchor “Read more about SEO strategies” is a bad idea. It gives a signal that the page you are linking to is the one that should rank for the keyword not the one you are optimizing it for.
✅ 9.2.8 Internal links – do you link to the page you are optimizing?
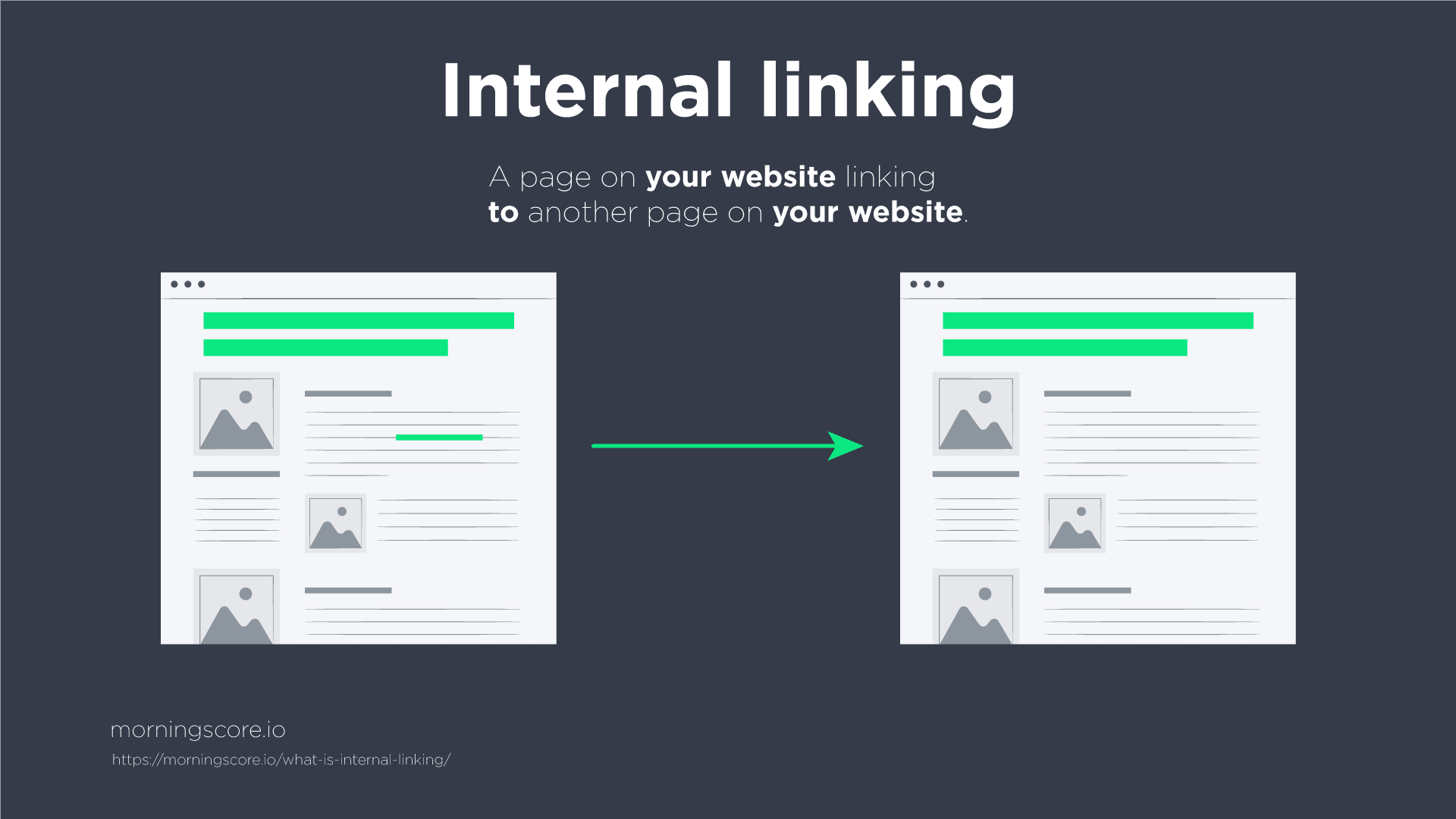
Get your landing page priority list and get all the keywords you are using to optimize a specific landing page. Now search through your website for the main keyword and the secondary keywords and link to the page you are optimizing from each page where the keywords are mentioned.
You can use Google to find this by searching:
site:domain.com “keyword”
Each page should have a good amount of internal links from other pages. In case you don’t use the keywords on other pages, add small pieces of content in pages from similar categories and link from there.
Or, instead you can search to find other pages from your website ranking for the keyword by searching which isn’t necessarily mentioning the exact keyword:
site:domain.com keyword
✅ 9.2.9 External links – do you link to other websites?
External links are important for Page Quality. By adding a link to a relevant, authoritative website to your content, you are showing both the user and search engines where you got your information from and where the user can go to read more about the topic.
Pages that link to external sites rank higher than those that don’t but link only to relevant content on trustworthy websites.
✅ 9.2.10 Optimize for featured snippets, Q&As and reviews
We won’t go in depth here but, schema markup can be used in many ways to mark up your page content and get you shown in featured snippets above the top ranking websites or in the related questions box.
This is a nice way to bypass the ranks and be displayed above everyone else.
Other than using Schema markup, you can optimize your content for features snippets.
If the content contains questions you should make it clear that there is a question and what the answer is. Make sure to have an objective answer to the question without “if’s” – be confident, straight forward and neutral.
✅ 9.2.11 Is your content long enough?
If Morningscore is marking your landing page as having a low word count you should probably add it to your future content list under content expansion.
The problem with low word count is that your page will have difficulty ranking if there are less than 400 words. Not because of the word count itself, but because you most likely doesn’t cover the full subject around the keyword with only 400 words.
Be critical of this issue, because some pages are not meant to rank and it is not necessary to put too much energy in content expansion (most common we see with this problem is the “contact” page).
If the content on your category pages and blog posts is 400 words or less I can almost certainly say that your content is way too thin.
Get inspiration from outside of your niche and check category pages in competitive niches and find out what they do.
A clue: scroll to the bottom of the page and see the content.
The exception is if the ranking pages are huge brands. Amazon, Nike, etc. often don’t need that much content because of their website authority so don’t use huge brands as inspiration for content.
Look for the websites competing with the huge brands.
For category pages you should aim for at least 800 words or more. For blog posts it might take as much as 1.000, 2.000 or 3.000 words depending on the subject.
Link building strategy/plan

Link building is still an important part of SEO in 2024 and it will be very difficult for your website to rank without any backlinks.
What you are interested in are dofollow links from websites with a high Domain Authority and/or high relevance for your niche.
10. Link analysis
It all starts with a proper analysis. Here you find out what your current backlink profile is and find link building opportunities.
✅ 10.1 Prepare a file for link building opportunities
Make an excel file or Google sheet where you will add the link opportunities you find. Name the columns URL, DA (for domain authority), Contact (to add the mail of link to contact form), Status (color coding for easier overview – red for dead end, yellow for in progress, green for link received) and Notes.
The type of links we will be adding are mentions, lost links for reclamation, easy competitor links and outreach suggestions
✅ 10.2 Check out your mentions
There are plenty of SEO tools that help you track down your mentions. Here we explain how to do it with Morningscore.
If you haven’t already, add your brand name to the Morningscore keyword tool.
Right click on it and “See all ranks”. Look through the SERPs and try to find websites that mention your company/brand but do not link to your websites.
For now just add the URL to your link building opportunity list.
Another option is to head to Google and search “your brand name” – remember to add ” before and after your brand name to search for results mentioning that on their page.
✅ 10.3 Reclaim your lost links
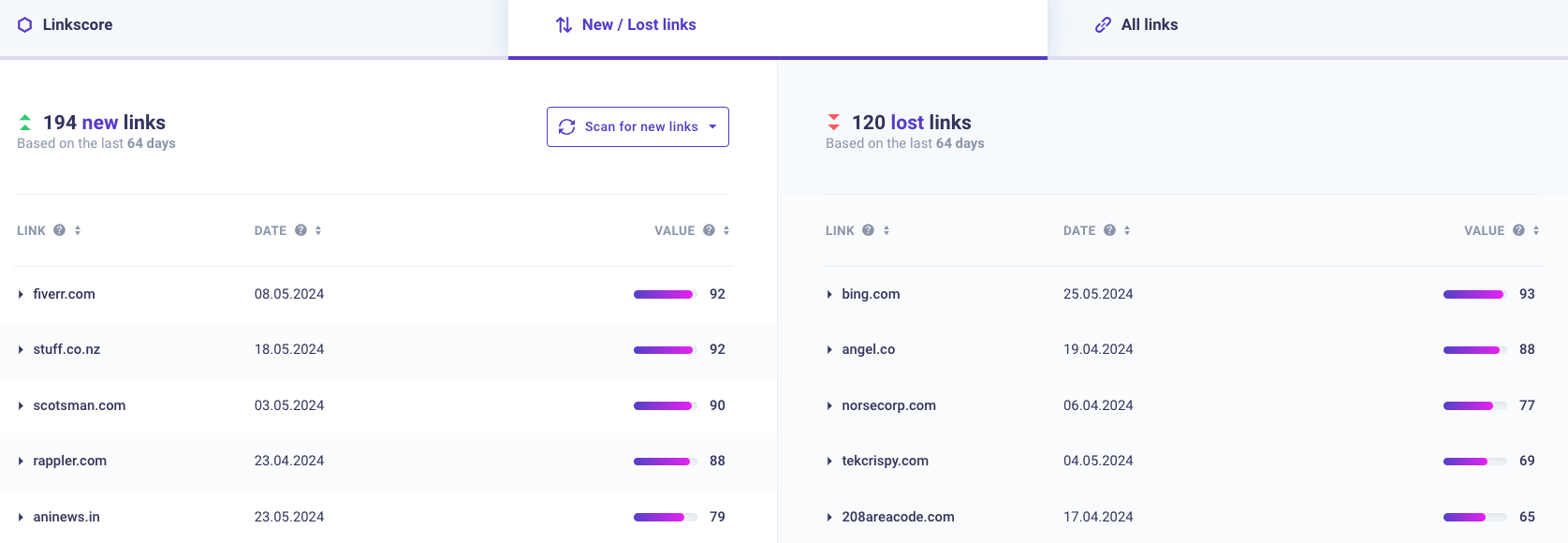
In morningscore, set the time period to show data for the past two months (or another timeframe you want to work with).
Check the domains listed in the lost links list and note down those that have a high DA or is highly relevant no matter the DA.
It is easier to contact a website and have them put your link back than it is to reach out to a website that has never heard of you before and have them link to you.
Make sure to verify that the link to your page is gone by clicking into the page that is/were linking. In some instances, it’s a false positive and the link isn’t lost in reality.
✅ 10.4. Get the low hanging fruit from the competitors
Add your competitor’s website to morningscore as a competitor.
Go to All links and export the complete data.
Do this for as many competitors as you want.
Put all data in the same file and sort by DA. Then remove any entries with a DA below 10 (or whatever limit you want). Sort afterwards by the Nofollow column and remove all entries where nofollow is TRUE.
Use conditional formatting to change the background color of the data field in the URL column if the data is a duplicate.
This should mark all the duplicate URLs in your list and give you an overview of websites that more than one of your competitors are getting links from. Chances are that these are company or profile directories and very easy to get.
✅ 10.5 Get the outreach opportunities from you competitors
After you added all the low hanging fruit from your competitors’ link data feel free to remove the duplicates (you can also make a copy of the file before you do so you keep all the data).
The next step is a bit labor intensive but well worth it.
Check each link and try to find out how you could get the link from the same site.
Is it a newspaper article and could you contact them when an important event happens in your company? A blog article whose owner you might be able to contact? Maybe it was a website that likes to post guest articles that you could write?
Add all these opportunities to your list for future outreach.
✅ 10.6 Scrape the SERPs
This step depends on what kind of business you are running and what your product is.
As an example, a hairdresser will focus on local influencers writing about hairdressers in the area (“best hairdresser in Plymouth”), local newspapers and local directories, while a company that sells a WP plugin to the global market can go after any blog doing plugin reviews or comparison lists in the last year or two among other link building opportunities.
So try and figure out where you fit in and how to find people that are writing about the product or service you are selling.
When you find these articles, make sure that the link is dofollow before you put energy into trying to contact the writer. Right click on the page and choose inspect. Clicking on the link should highlight its code and if you see rel=”nofollow” written inside the <a> tag don’t bother with this link. All the rest you should add to your list.
✅ 10.7 Manual SERP searches
Another way to research and find easy and free link building opportunities is the old school manual way using Google commands.
Head over to Google and simply search for “add link”, “add website”, “add company” and similar ideas you can think of to find websites, often directories and maps, that you could get a link from – or simply search for “free link building opportunities” to find guides and PDFs containing exact links to pages that you can easily create links from yourself.
11. Outreach
✅ 11.1 Reach out to reclaim lost links
Write an email saying you noticed that the link went missing and offer them help in fixing the problem.
After all, it might be a mistake that they didn’t know and you might even notify them about a website issue they need to fix.
✅ 11.2 Reach out to mentions
I like to start the mail by thanking them for mentioning us, writing a review about us (bad or good) or naming our product. It is important to start the mail on a positive note and make them feel appreciated. Then continue with asking if they mind including the link.
This type of mail is a bit more personal than the other outreach mail types.
Do not act spammy though. Your email will for sure end up in the trash if it sounds the tiniest bit like an automated email.
✅ 11.3 Cold mail outreach
This type of outreach has the lowest chance of being successful. So I like to put in sufficient time to write nice, but universal mail that I can send out one by one with minimal change.
This will speed up your outreach as it can take a while to come up with a perfect angle to approach people with a cold email.
You can also send these emails in waves and adjust the content based on the reactions.
Again, spend time on perfecting your email and make it sound like an actual human writing it. Your email will end up in the trash if it sounds automated, generic or over personalized.
✅ 11.4 Be mindful of the anchor text
Hopefully the outreach gave some positive results. Now you have one more thing to be mindful of – the anchor text.
When building links don’t use too many exact match anchor texts. Exact match anchor texts are those that are exactly the same as your main keyword for the landing page you are building a link to.
Similar to that you have partial match anchor texts that use a part of the keyword (a keyword can be made up of more than one word) in combination with other words. Exact and partial match anchor texts shouldn’t be used in more than 15% of your link profile.
Most of the links you build should have generic anchor texts (URL, brand name, “click here”, “read more” etc.).
Why do you need to be aware of the use of anchors?
The anchor text is what Google sees on the link and expects the page to be about that. The thing is that active link building basically is against Googles guidelines.
One of the ways to expose manipulation is the anchors. It’s unnatural that everyone would link to your site naturally using the keyword. In most cases the link would be a plain domain link and not on any anchor – especially not the keyword.
12. Maintenance
Once you are done with previous optimization steps you will be combining link building, continual content optimization and maintenance.
✅ 12.1 Keep an eye on new updates
Google comes with new algorithm updates regularly and these updates can shake up the ranks.
You can be proactive and follow various blogs that will write about the changes as they roll out or you can play detective when you notice a drop in ranks and try to fix any collateral damage the update might have caused.
✅ 12.2 Changes in keyword search volume
Keyword search volume depends on the number of people searching for a specific keyword, so of course there will be some fluctuation in the number.
Big changes can also happen following search trends and no matter the reason why the search volume is changed you will possibly need to adjust your content or make a new landing page for a keyword whose search volume suddenly jumped.
✅ 12.3 New competitors entering the market
Companies come and go. There might be companies going bankrupt and leaving a hole which you might want to fill.
But there might also be new companies that invest more into SEO than your old competitors. Be sure to use their data with the strategies we mentioned previously and monitor the upcoming competitors closely.
✅ 12.4 SEO of new content
Any new landing page you make as a part of your content strategy will need to be optimized and checked before and after publishing.
It is of course best if the content is fully optimized before publication as once the search engine has crawled and indexed it, there will be a while before another crawl.
If you have made changes to a page and wants it to be crawled faster you can go to your Google Search Console account, search for the landing page and request indexation.
✅ 12.5 Keep updating existing content
Keep your content ever fresh by adding new content, images, new links etc.
Make sure that the existing information is accurate and up to date.
Make sure to edit the update date when you edit pages. If you radically change the content you can even change the publish date.
✅ 12.6 Keep an eye on recently lost links
Lost links will keep popping up, so keep an eye on Morningscore so you can reclaim them as fast as possible.
✅ 12.7 Keep an eye on Morningscore health tool
Just because you are done now doesn’t mean new issues won’t pop up. You should run onsite SEO checks regularly.
External links can break, you may delete an image in your media library by accident or we might add more issues to track in a next update.
FAQ
What is SEO?
SEO is short for Search Engine Optimization. SEO is the process of getting higher rankings on Google by having a technical good website, great and relevant content and authority. SEO is the name for the optimizations on and off a website that make you rank on Google when people search for information, products or services.
Does my company need SEO?
Almost every company need SEO. Google is the most used searched engine and this is the place where most people start – and end – their buying journey. To take part of that and get sales and leads you need to be visible in the search engines.
How does SEO work?
SEO is simple and complex at the same time. In reality, it’s quite simple. SEO is about making your website aligned with what Google and the users are looking for – and how they look for it. Google uses web crawlers to scan the entire internet, hence it is an important part of your SEO strategy to make sure that your website is accessible for crawlers so they can access your content. There is a lot of factors that Google counts, but you simply needs to match the intent that users have, give a nice user experience and establish authority for your website.
What can I do to get more traffic from search engines?
To get more traffic you can either optimize your current pages, make sure to be more helpful, answer more question and cover the subject in depth. On the other hand, you can research and find new keywords and create new dedicated landing pages targeting the keyword.
How long does SEO take?
SEO kicks in after a few days or weeks in the beginning but to see the full results of your SEO work you can expect 6-12 months. Sometimes you reach the top for certain keywords quite fast, while others takes some time and ongoing optimizations but generally speaking SEO takes up to a year – at least to see the full effect.
How long should my content be?
How long your content should be depends of the type of page and the users intent – what are they looking for? For category pages I aim for at least 800 words and blog posts is often triple the amount or more depending on the subject.

