Page title, title tag, meta title – call it what you will. While it is a seemingly small detail, it can significantly influence your organic rankings in Google. Unlike meta descriptions, page titles are one of the important factors that Google uses to rank you in search results. If you want to understand what page titles are, you’re in the right place. Here, we’ll explore how the title tag can boost your Google ranking and guide you in creating the most compelling title tag.
A page title is an HTML element marked with the <title> tag and placed in the <head> section of the code. In SEO, title tags are the clickable headings shown in Google’s Search Results and browser tabs. These tags are crucial for both usability and SEO, and must be short, precise, and descriptive.
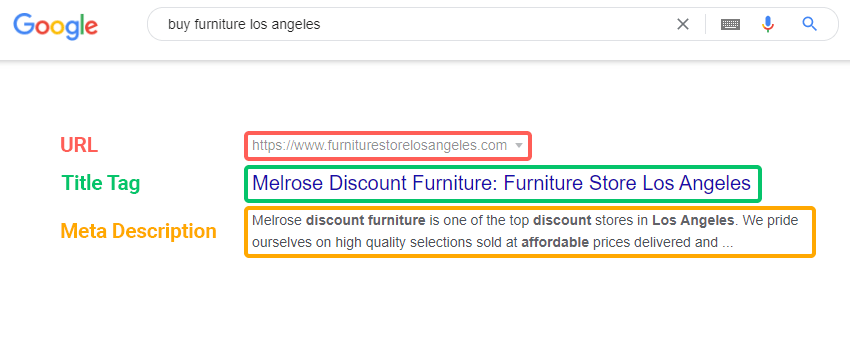
Your <title> tags are not the same HTML elements as your <h1> tags. While <h1> tags, also known as heading tags are shown on the page as the heading of your content, title tags are part of the meta tags hidden on the actual page. As such, your title tag and your h1 tag do not have to be the same.
However, that doesn’t mean you need to edit your website’s code because most modern CMS platforms have plenty of plugins for that. Not comfortable working with your website’s code? You can easily add or edit your title tags with a plugin like Yoast SEO in WordPress.
How do title tags affect SEO?
The page title is an integral part of your Onpage SEO. In the Search Results, it is shown above your meta description and under your URL. To compete effectively in SEO, optimizing your page titles is crucial for both search engines and end-users.
Title tags are important for SEO because search engines use them to understand the contents of the page. Title tags also influence the user’s decision to click on your page in the Search Results. Great page titles not only promote the content but also encourage users to click on them.
On the one hand, you can look at title tags as your little promotional space in Google’s Search Results. Here, your goal is to create an incentivizing and relevant “offer” for the end-user that essentially gives them a good reason to click on your page.
Consequently, being one of the highest HTML elements by hierarchy, search engines use page titles as a strong signal to derive meaning about the page’s contents.
A page’s title can make or break the SEO performance of a page. Underoptimized page titles that search engines do not understand or those that don’t resonate with the user get demoted in the Search Results. In addition, if your title tag doesn’t live up to Google’s standards, it won’t be shown in the SERPs (Search Engine Results Page). In contrast, well-optimized page titles help search engines correctly classify and rank the content while simultaneously providing value to the end-user.
How to write the perfect page title tag?
The primary goal of a title tag is to get the user’s attention and present your pages more attractive than your competitors’ pages. Doing this ensures that users find more value from your page than other pages, leading to more clicks. Because your title tag’s content depends on your actual target keyword and its Search Intent, you need to create unique titles for each page.
Use these 13 tips to write more effective title tags:
- Use your primary keyword in your title tag
- Include your brand name where possible
- Write titles for people and not search engines
- Avoid title tags shorter than 20 characters
- Don’t write titles longer than 60 symbols
- Use a compelling Call-to-Action (CTA) that provides a reason to click
- Stand out from competitors with emojis
- Use common abbreviations smartly to save space
- Match the Search Intent to get the user’s click
- Write titles that accurately represent the content of your page
- Create unique title for each page, avoid duplicate titles.
- Never automatically generate page titles
- Create a unique OpenGraph title for Social Media
Let’s break down each of these tips and examine how you can use them when creating title tags.
1. Use your primary keyword in your title tag
When writing title tags, it’s important to integrate your primary keywords. This is a vital step because search engines use your title tags to understand the content of your page. Additionally, keywords are crucial for users as they evaluate whether your page is relevant to their search query. Including a keyword that aligns with the user’s search directly will directly increase your click-through rate as the title is perceived as more relevant.
To optimize the effectiveness of your title tags, place your main keywords as close to the beginning as possible. Doing this will ensure that the user immediately recognizes the relevance of your page because our eyes scan websites in an F-shaped pattern. Moreover, doing so prevents any potential issues later if Google decides to change the length of title tags shown in the SERPs.
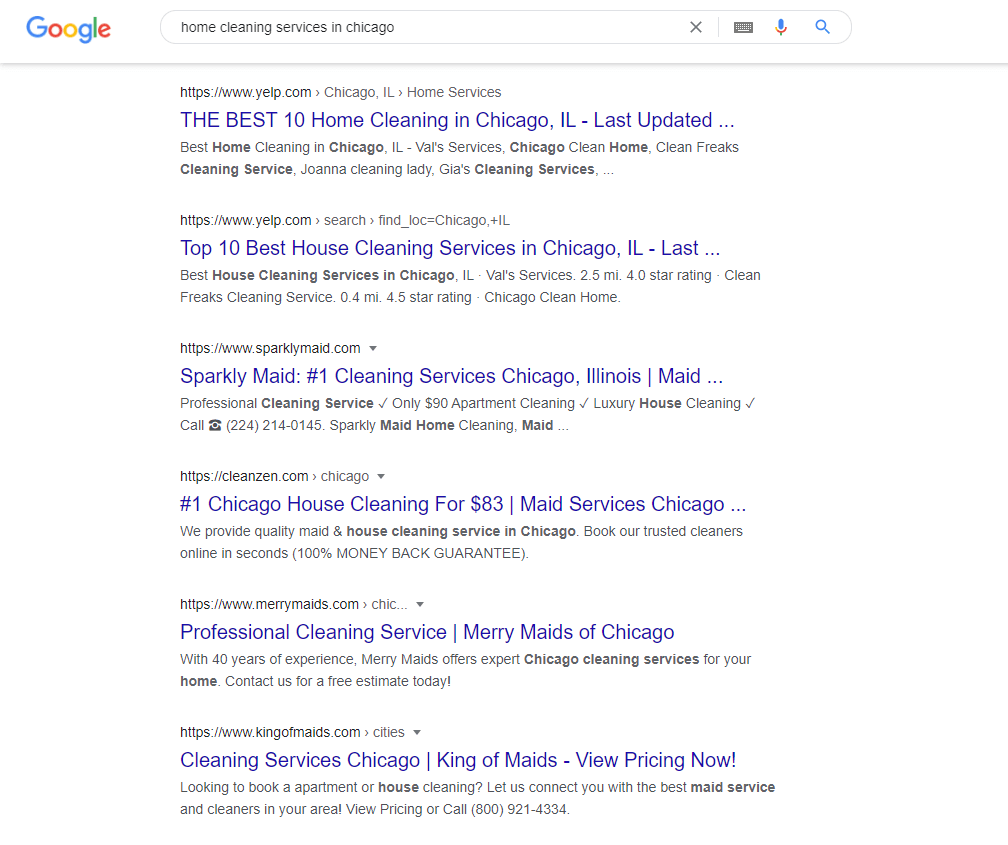
Take a look at this SERP, where the primary keyword is front-loaded in all of the 6 title tags on the first page.
2. Include your brand in your title tag where possible
If the length of your page title allows it, it’s always a good idea to feature your brand in the Search Results. That’s because using your brand in titles creates a positive feedback loop. Firstly, Google’s Search Results are a great tool for branding and can increase your brand awareness. Secondly, using an existing strong brand can increase your click-through rates, further improving your rankings.
For example, take Colgate’s blog.
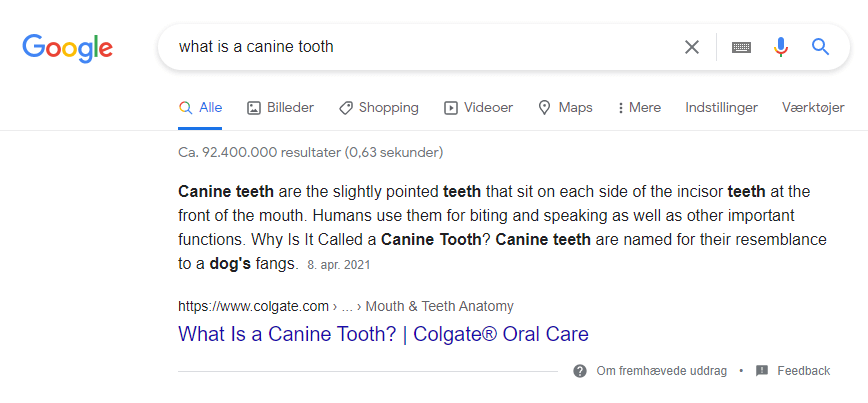
Because they have an existing strong brand, they have a clear incentive to add that to their page titles. As such, it generates awareness and authority with people who have never seen their brand – and brand evangelism among those who have previously used their products.
3. Write titles for people and not search engines
“Write for users, optimize for machines.” Like all other SEO practices, it’s essential to create pages and write content with the user in mind and not for the search engine itself. Write short and concise sentences that communicate a specific meaning without overusing your keyword.
Even if you manage to “trick” the search engine and get your page ranked high, this will only be temporary, as users will not resonate with or click on your results. Google measures those user signals, and in turn, it will eventually demote your page if it’s not perceived as relevant.
In contrast, you should use best practices from copywriting to write incentivizing title tags that get users excited and motivated about your page.
4. Avoid title tags shorter than 20 characters
Title tags shorter than 20 characters rarely communicate the point across and satisfy the user. In only 20 characters, it’s almost impossible to write something coherent that provides value to the user. As such, your short title tags can easily get overlooked by users who find your competitors’ longer titles more relevant, as they better communicate what to expect by clicking.
5. Don’t write titles longer than 60 symbols
Similarly, avoid writing title tags longer than 60 characters because Google cuts them off with an ellipsis. That’s especially important to remember if you have a long target keyword – as your value proposition can easily get lost. This can result in the user not finding much value in your result – because they literally cannot see the text that communicates it. You can test if your title tag has the right length with Morningscore’s title tag checker.
6. Use a compelling Call-to-Action (CTA) that provides a reason to click
It is vital to make your title tags actionable to get the user’s click. You can do that by explicitly adding a Call-To-Action – or more subtly highlighting something of value. For example, if you offer “emergency road service,” you can subtly communicate your call-to-action with a copy like “Pickup in less than 30 min.” Similarly, an explicit call-to-action is something like “buy now” or “compare here.”
7. Stand out from competitors with emojis
Emojis are a great tool that you can freely use when creating page titles. That’s because they create contrast in the search results and help your page stand out from competing pages. However, keep them relevant and don’t just randomly use any emoji – as they can have double meanings.
While emojis can enhance visibility, excessive use can make your brand look unprofessional and put some users off. Google doesn’t show all emojis but only a tiny subset of them. For example, dentists can use the “tooth” emoji, and hairdressers can benefit from the “scissors” emoji, as both are highly relevant in their respective contexts.
8. Use common abbreviations smartly to save space
Because of the limited space available, it’s a good idea to use some abbreviations, shortenings, and numbers where it makes sense and possible. For example, you can shorten “without” or “versus” to “w/o” and “vs.” respectively if they are part of your value proposition.
However, keep in mind that it’s probably best not to shorten words that are part of your actual target keyword. Although Google’s BERT algorithm update understands search queries better, it can still be somewhat limited, especially when handling queries containing adverbs like “without.”
9. Match the Search Intent to get the user’s click
Users search because they have a need that has to be solved. Whether it’s a problem they need the solution to, a product they are looking for, or directions, they have a concrete outcome in mind of what they need to see.
Because Google recognizes that, it tries to answer that search query as close as possible to the outcome the user envisions in their mind. As such, for you to rank high on Google and maintain your rankings, you must understand the concept of Search Intent – and apply it in your title tags.
Your title tags are the strongest deciding factor when users search, as it’s the most prominent element from your page on the Search Result pages. Understanding your target audience and the nature of the search helps you bridge that gap and create unique page titles that satisfy the user’s needs.
10. Write titles that accurately represent the content of your page
Getting the click is only one part of the equation; retaining users on your page is equally crucial. If you oversell the contents of your page, you run the risk that users will quickly exit and never return. From there, things go downhill even further. You lose a potential customer, and the user’s digital behavior signals tell Google other pages are more relevant – as users stay around there for longer. It can also create a negative effect over the long term, as Google can decide to demote your content in the Search Results.
11. Create unique title for each page, avoid duplicate titles
In addition to thin content, duplicate content in your page titles is a clear no-go, as it has the potential to confuse both users and search engines. Because of that, you need to create unique page titles that match the unique content on the page, while also catering to the Search Intent specific to that page.
12. Never automatically generate page titles
Most popular Content Management Systems have plugins that help you automatically generate page titles based on conditions like the name of the product and your brand name. While this can look incentivizing at first as it saves you time and effort, it’s usually a bad idea. Auto-generated title tags tend to appear generic and uninspiring, potentially resulting in a loss of clicks and rankings over time.
Because of that, you want to create a unique title tag for every important landing page, category, or even product page. This way, you can stand out from the competition and get the user’s click.
13. Create a unique OpenGraph title for Social Media
It is worth repeating, when we create page titles, we aim to satisfy the user’s Search Intent as best as possible. But here’s something else to consider: how your pages look when shared on social media. Tag titles that work well for search might not be as appealing on social media. By default, social media sites use general information from your page if you haven’t specified OpenGraph meta content, but it’s not as confusing as it may sound.
Here is a guide on OpenGraph meta content that shows how to create captivating titles for social media. Make your titles exciting and engaging for social media to potentially attract more traffic. If you’re using WordPress, you can easily achieve this with the “Yoast SEO” plugin.
What makes a title tag good? Three examples of great page titles for SEO
Anyone can write a page title. However, crafting great SEO headlines is an in-depth skill that requires understanding your target audience, having experience with copywriting, and knowing the best practices from SEO. Additionally, you rarely write the perfect page title from the first try, and you typically need several iterations until you create just the right one.
The most important factor for a page title is matching the Search Intent of the end-user. Good page title tags contain a maximum of 60 characters, unique and relevant content, close variants of the target keyword, and a Call-To-Action. Thus, good title tags incentivize the user to click on them.
Now, I’m a strong advocate of learning from examples – so let’s briefly look at three great examples of title tags. We’re also going to break them down, looking at what exactly makes them effective from the factors we mentioned above.
Title tag example #1 – Informational searches
When creating a title tag for an informational search, you can provide the user with a good reason to click by addressing a “hidden meaning” or a problem the searcher has in mind. For example, take a look at the top result for the query “which plants are carnivorous.”
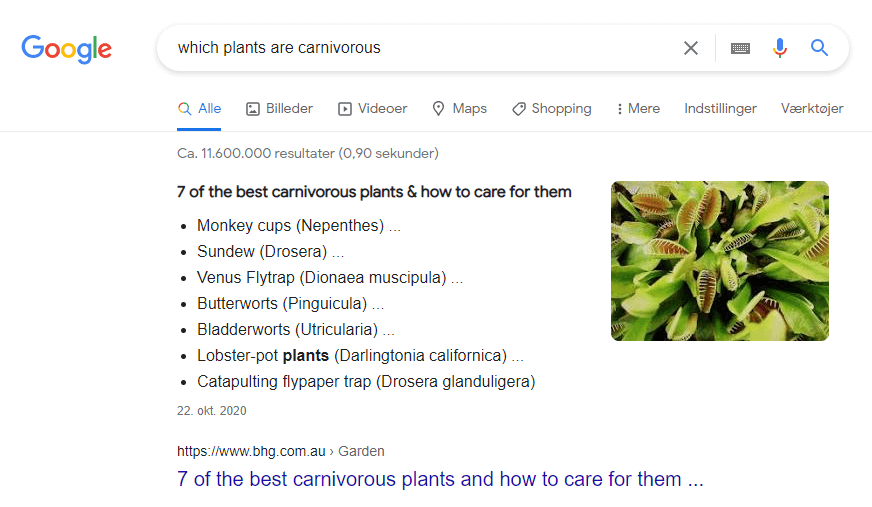
In that particular example above, we can see the author has achieved just that. Because the website owner understands their target audience, they know people searching for this query are interested in owning a carnivorous plant at home. As such, their unique take on the article is “how to care for them.” Ultimately, this bet (and effort in understanding users) has paid off, as they rank well for that keyword.
Title tag example #2 – Inspirational searches
For search queries seeking inspiration, a great way to stand out and get more clicks is to show the number of examples in your article. Alternatively, you can showcase the names of famous designers that are the source of inspiration, which you’re featuring in the post. Here, let’s look at an example of the keyword “interior design examples.”
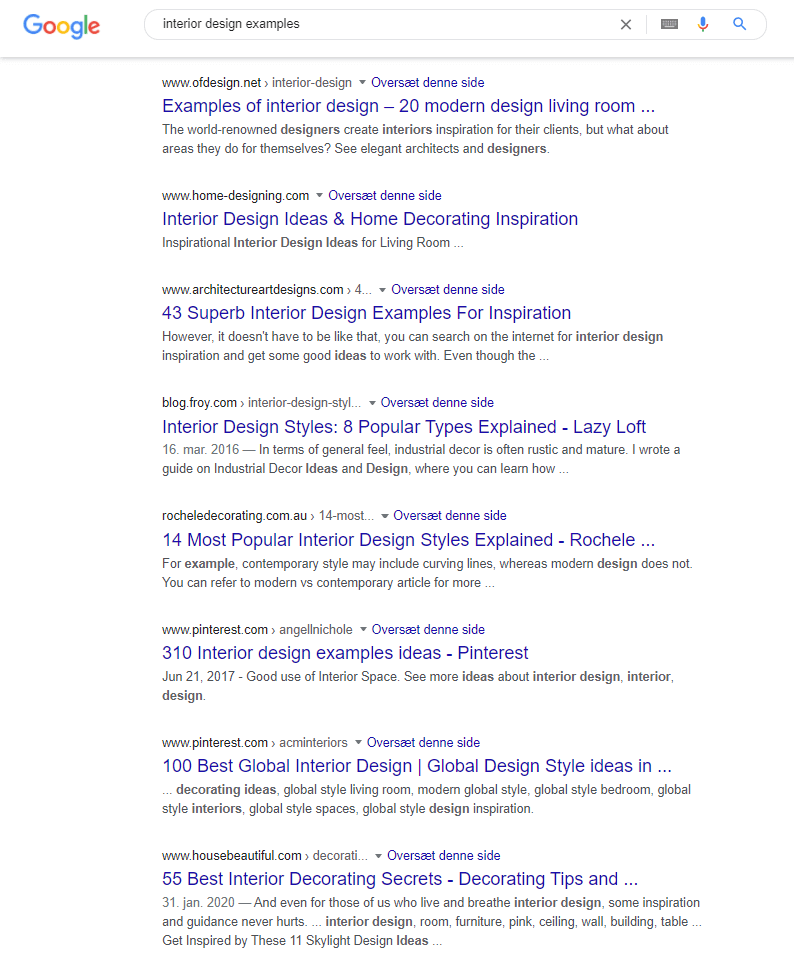
As you can see in the example above, this is precisely what’s happening in the current Search Results. Seven of the 8 title tags shown in the image above contain a number.
Title tag example #3 – Transactional searches
When it comes to commercial keywords, incorporating details such as discounts, stock availability, return policies, warranties, etc., into your page titles can be highly effective. This is because you provide users with a clear and explicit Unique Selling Point that resonates with them. Even if you opt-out of any discounts or special offers in the page title, you can (and should) still feature some of your softer USPs, which could include features that appeal to emotions, values, or overall positive experiences.
For this example, let’s look at the keyword “buy running shoes.”
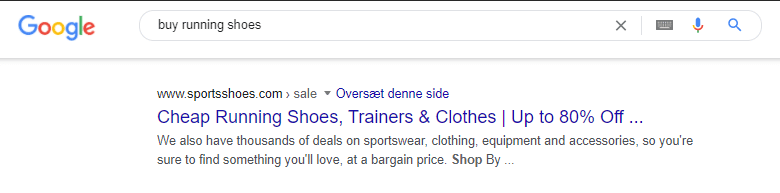
As seen in the image above, this website is using exactly those tactics, where their title tag features hard USPs like “up to 80% discount”. At the same time, their meta description focuses on softer USPs that make the user feel good, like “thousands of deals,” “sure to find something you’ll love,” and “at a bargain price.”
How long should title tags be?
The length of your title tags matters because lGoogle shortens long titles and replaces them with an ellipsis. In turn, this can result in your page ranking badly because it is not encouraging enough for users to click on it.
Ensure your page title is no longer than 580 pixels (approximately 60 characters) since Google shortens longer titles. Shortened titles may lack the main value proposition or call-to-action, making them less appealing to users and resulting in fewer clicks.
Because every character from the alphabet has a different width in pixels, you can use the 60 character mark as a rule of thumb. However, remember that other elements like capital letters and emojis can also count as 1 character but use more pixels. From experience, we recommend using some free meta tag length checker. Such tools show you exactly how long your title is in pixels and where it gets cut off by Google. Two of our favorites are SERPSim & MetaTags.io.
Keep in mind that Google often experiments with title tag lengths. Because of that, you want to upfront-load your title tags with your target keywords and most important information. Any additional details should come after that, as Google can potentially shorten titles in some future update.
Optimize your title tags and get better rankings and more traffic
Your page title tags are some of the most influential Onpage factors in your efforts with SEO – which only justifies the time and time and effort it requires. Optimized title tags get top placements in Google and ensure that the user decides to click on your page over others in the Search Results.
Have any additional questions about title tags? We have collected the most common questions here:
How does the length of a title tag affect its visibility on mobile devices versus desktop devices?
The visibility of title tags on mobile versus desktop devices can vary due to screen size limitations. Mobile devices, with smaller screens, may truncate longer title tags more aggressively than desktop browsers. Therefore, prioritizing key information at the beginning of the title tag is crucial for mobile visibility.
Are there any specific industries or types of websites for which the advice on title tags might vary?
Industries with unique search behaviors, such as e-commerce or local businesses, might need tailored advice on title tags. For instance, including price, brand, or locality might significantly impact click-through rates in these sectors.
How do search engines other than Google, such as Bing or DuckDuckGo, treat title tags?
Search engines like Bing or DuckDuckGo also use title tags to understand and rank webpages, but their algorithms and the weight they assign to title tags may differ from Google’s. Optimizing for Google often aligns with best practices for other engines, but it’s worth researching specific guidelines or differences each search engine might have.

