If you’re new to SEO and have a website, an online shop, or a blog, or just want to learn more about what SEO is, how it works, and what to do, you’ve come to the right place to get started with search engine optimization.
Search engine optimization, even for beginners, is a crucial discipline when it comes to increasing your online presence and getting your website to rank high on search engines like Google. In this guide, we will explore all aspects of SEO, from basic concepts to more advanced techniques.
Whether you’re completely new to SEO or already have a basic understanding of it, this post will give you the insight and expertise to improve your website’s visibility and attract more traffic. So let’s dive into the world of SEO for beginners!
Introduction to SEO for beginners

SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is a method of improving a website’s visibility in organic (non-paid) search results on search engines like Google. When people search for relevant keywords, the goal of SEO is to make your website rank higher on the results pages, increasing the chance of users clicking through to your site.
SEO is a crucial step in reaching your potential customers and increasing traffic to your website. It’s not just about manipulating search engine algorithms, but rather creating a user-friendly and informative website that delivers valuable content to your visitors.
Many SEO agencies, consultants, and freelancers like to tell SEO newbies that SEO is so incredibly complicated that you can’t do it yourself. You have to pay them $150/hour or you can forget about being found on Google.
Let’s start by debunking that myth.
SEO is as complicated as people make it out to be. Sure, there are elements of SEO that are complicated. If you’re really going to geek out and be a hardcore SEO expert, it also requires a certain level of technical expertise and basic programming skills.
With this post for SEO beginners, you’ll get really, really far on your own and if you implement it all, I have no doubt that you’ll get some top rankings, page 1 rankings and have a generally very good starting point and probably a lot of traffic.
When you eventually reach a point where your own skills run out, you can get external help with the final technical elements, a skilled copywriter to hone your message, or get a few more relevant links.
Technical SEO for beginners
Even if you’re not technically inclined, there’s a good reason to keep reading. Technical SEO can sound difficult if you’re a beginner and don’t have a background in IT.
However, the technical part is the foundation for both the functionality of our website and our future success with search engine optimization. We cover the basics of technical SEO so that you, as a beginner or intermediate, can join in.
Crawling and indexing
Crawling and indexing are two important processes in Search Engine Optimization (SEO) that help search engines understand and organize the content on the web to provide relevant search results to users. Let’s take a closer look at how these processes work:
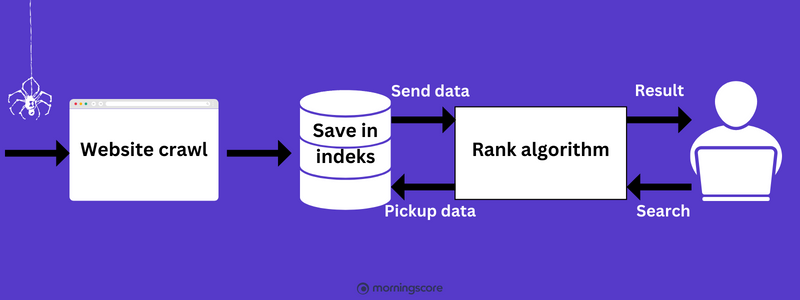
Crawling:
Crawling refers to the process in which search engine bots, also known as “spiders” or “crawlers,” crawl the internet to find new and/or updated existing content on various websites. These bots typically begin their journey from the search engine’s own database of URLs, also known as a crawl queue or crawl seed.
When they find a URL, they visit it, follow internal links on the page, and navigate to other pages. This is repeated over and over again, creating a list of landing pages that the search engine has crawled or visited.
The goal of crawling is to find as many relevant landing pages as possible and update the content regularly to ensure that the search engine results are as current as possible.
Indexing:
Indexing is the next important phase after crawling. When search engine bots visit a landing page, they analyze its content and structure. The information they find is then organized into a large database called a search engine index. The index acts as a comprehensive list of all the words, phrases, and other relevant information on each URL.
Indexing also identifies the important keywords on a page, which helps the search engine understand what the page is about. This information is later used when a user performs a search to match relevant pages with the search query.
Here are 4 great beginner SEO tools:
Morningscore
The All-In-One Solution: Monitor your organic rankings with our rank tracker, monitor your site health with our SEO website checker, view your links in the backlink tool, and create missions and follow through to improve your rankings.
Google Search Console
Monitor your site’s indexation, get notifications with error messages from Google, and monitor your keyword performance. Go to Search Console.
SEO Site Checkup
A great tool for beginners to check the overall health of your site. Go to SEO Site Checkup.
Woorank
Monitor your keywords, check your site health, and create reports. Go to Woorank.
Sitemaps and the importance of having one
A sitemap (also called a “map of the website”) is an XML file that contains a list of all the pages, content, and structures on your website. This file format is specifically designed for search engines and helps them understand the overall structure of your website and find all its important pages.
A sitemap is important for SEO for several reasons. SEO for several reasons:
- Improves crawling: Once you’ve created a sitemap, you can submit it to search engines like Google. This lets them know which pages are available on your website and allows them to crawl and index them more efficiently. This way, you ensure your pages are visible in search engine results.
- Optimizes crawl budget: Search engines have a limited amount of time and resources to crawl and index your website. A sitemap helps optimize this crawl budget by telling the search engine which pages to prioritize.
- New page discovery: When you add new pages or content to your website, it can take time for search engines to discover them. With a sitemap, you can instantly inform search engines about the new additions so they can index them faster and show them in search results.
To create a sitemap, you can use different tools and plugins depending on the platform your website is built on. Once you have created it, you can submit it to Google Search Console.
Optimizing robots.txt file
It’s not unlikely that this is the first time you’ve heard of a robots.txt file. It’s a bit of a technical nerdy thing, but nevertheless, it’s super important for the indexing of your pages in search engines – even if you don’t even know you have a robots.txt file today.

The robots.txt file provides instructions to search engine bots on which parts of your website to crawl and index, and which to ignore and not index. It’s important to optimize this file correctly to ensure that search engine bots can access all relevant pages on your website and that you make sure they don’t crawl and index the pages you don’t want them to find on Google.
But shouldn’t all your pages be indexed on Google, you might be thinking? The answer is no, not necessarily.
There will be a number of pages that you can tell Google’s bots not to index by disallowing them because they have no purpose in the search results or the content on the page is of such poor quality or relevance that it has a direct negative impact on your page’s performance in Google’s eyes.
An example of a page you should ask Google not to index is your terms and conditions page. This could also include your privacy policy page.
Find your robots.txt file by typing: YourWebsite.com/robots.txt
Load speed
You might know it yourself. You click on a page that loads for what feels like hours. Your patience runs out and you leave the page before you’ve even visited it.
A slow page load is really bad usability and Google doesn’t reward bad usability.
Besides the negative effect on Google, it will also directly affect your online sales. The faster your website is, the more conversions you get.
There are many things that affect your site’s load speed and therefore it’s impossible to say exactly what you should do. It has to be assessed from website to website, but some of the elements that slow down your website are:
- Image size and compression: Larger images take longer to download. Optimizing the image size and compressing the image files can help improve load speed. Compress your images with a tool like tinypng.
- Server performance: A slower server will take longer to process requests and deliver pages to visitors. A fast and reliable server is essential for a good load speed.
- CSS and JavaScript files: Large and unoptimized CSS and JavaScript files can increase load time. Minimizing and aggregating these files can improve performance. This is quite technical and may require the help of a web developer/programmer.
- Browser caching: Taking advantage of browser caching allows visitors to store resources locally so they don’t have to retrieve them on every visit to the site.
- Website hosting: Choosing a reliable and fast web host is crucial for load speed.
- Responsive web design: A page that adapts to different screen sizes and devices can have a better load speed as it provides optimized resources for each device.
- HTTP requests: Too many individual HTTP requests for resources, such as scripts and images, can increase load time. Reducing the number of requests can improve load speed.
- Server caching: Implementing server caching can improve load time by providing static pages instead of generating them from scratch for each request.
- Redirects: Too many redirects on a page can lead to extra requests, increasing load time.
- TTFB (Time To First Byte): TTFB is the time it takes for a browser to receive the first byte of data from the server. A low TTFB should be the goal for a fast load speed.
Content Delivery Network (CDN): Using a CDN can reduce the geographical distance between the server and the user, which can improve load time.
Beginner tip: Test your website’s load speed here.
Mobile-friendliness and responsive design
Mobile-friendliness refers to how well a website works and displays on different mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. A website is designed to adapt to different screen sizes and provide an optimal user experience when visited from mobile devices.
There are several good reasons why your website should be mobile-friendly. Especially in terms of SEO:
- User experience: With more and more people using mobile devices to browse the internet, it’s crucial to provide them with a good user experience. If your website is not mobile-friendly, it can be difficult to read, navigate, and interact with on small screens, which can lead to a negative user experience and ultimately lower rankings on Google.
- Google’s mobile-friendly indexing: Google and other search engines prioritize mobile-friendly web pages in their search results, especially when searches are performed from mobile devices. Google has even switched to mobile-first indexing, meaning it primarily uses the mobile version of a webpage to assess and rank the content.
- Local SEO and mobile searches: Mobile-friendliness is also critical for local SEO. Many users conduct mobile searches to find local businesses or services near them. If your website is mobile-friendly, you increase your chances of appearing in local search results when potential customers search for something in your area
Beginner tip: Test your site’s mobile-friendliness here.
SSL Certificate – Secure your site

A Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate is a digital signature used to secure the connection between a user’s web browser and a website. It works by encrypting the data sent between the user and the website, making it difficult for unauthorized parties to intercept or steal information.
SSL certificates are important for several reasons:
Data protection: SSL certificates protect personal information such as login details, card details, and other sensitive data while it is being sent over the internet. This helps prevent this information from falling into the wrong hands.
Authentication of the web page: SSL certificates also contain information about the identity of the website. When a user connects to a secured website, they can check if the certificate is valid and if it matches the real website. This helps avoid malicious websites that try to impersonate legitimate sites to trick users.
SEO benefits: Search engines like Google prioritize websites with SSL certificates in their search results. Having an SSL certificate can therefore improve your website’s visibility and ranking in search results.
Customer trust: When users see a padlock icon or “https://” in the address bar, they feel more comfortable staying on your website. SSL certificates signal that you take security seriously and protect your users’ data.
Check if your website has an SSL certificate here.
Structured data (Schema markup)
Structured data, also known as “schema markup,” is a type of metadata that is added to the HTML code of a web page to help search engines like Google and Bing better understand the content of the web page. It is used to define different elements on your website so that Google better understands the content, such as products, reviews, events, and organization type.
Adding structured data to a website helps search engines understand the relationships between different data elements, making it easier for them to index and display the data in search results in a more relevant and visually appealing way.
The benefits of structured data for SEO:
- Improved visibility: By giving search engines a better understanding of the content on a website, structured data increases the chance of the page appearing in special search results such as Featured Snippets or Knowledge Graphs.
- Better understanding of content: Structured data helps search engines better understand the structure and content of the page, increasing the chance of pages ranking for the right keywords or terms.
- Preparing for the future: As search engines become more advanced and use AI and semantic analysis, structured data will play an important role in providing the necessary context and understanding of content.
OnPage SEO techniques for beginners

Before we go any further: kudos to you for joining us yet. Granted, most people don’t find technical SEO very exciting, but it’s super important to have the foundation, the basics, in place before building with content.
In this section, we will focus on OnPage SEO for beginners, which is all about optimizing the content on your landing pages.
Choose the right keywords
First and foremost, it’s important to perform thorough keyword research to identify the keywords your potential customers are using to find services or products like yours using a keyword management tool. The whole idea of keyword research is to make connections between:
- The words (content) we write on our landing pages
- The words users use to find the products or services you offer
In this context, it’s important to point out that you can’t optimize your pages for all keywords. You need to write the texts for the keywords that are relevant, that users use, and that creates value for your business.
Let’s take an example:
Imagine you run an animal health blog whose sole purpose is to inform. You don’t make money by selling a product, but instead have an income in the form of advertising spots on your website.
In the context of animal health, you will most likely write about dog food. For example, an important keyword for you is “what should a dog not eat”, but the keyword “buy dog food online” is not relevant for you because you don’t sell anything.
Beginner tip: Find the right keywords with a keyword research tool.
Create relevant content
To attract users, it’s important to create relevant and valuable content. Focus on answering questions, solving problems, and providing information that is valuable to your visitors.
So what is good and relevant content? Pages with +3,000 words? Not necessarily.
Today, it’s not about the quantity of text, but the relevance, quality, and whether the topic is covered in depth.
In other words: Keep your blog posts, category pages, and product pages short, concise, and comprehensive. If you do this, the amount of text will come naturally and naturally.
It doesn’t hurt you to write 3,000 words if that’s what it takes to write comprehensively on the topic but don’t make text length a goal in itself.
SEO-friendly URLs

SEO-friendly URLs refer to web addresses (URLs) on a website that are structured, descriptive, and easy to understand for both humans and search engines. Your URLs should be made to give a clear indication of the content of the associated landing page.
SEO-friendly URLs often contain relevant keywords or descriptive words that give users and search engines an idea of what they can expect to find on that page.
To create SEO-friendly URLs, you should follow these principles:
Relevant keywords: The URL should contain relevant keywords that reflect the content of the webpage. This helps search engines understand what the page is about and improves relevance in search results.
Short and sweet: Avoid long and complex URLs. Short URLs are easier to read, remember, and share. They also give a clear and concise indication of what users can expect to find on the page.
User understandable: The URL should be easy to understand for a person reading it. Avoid the use of cryptic characters, many parameters, and spelling mistakes. For example, avoid special characters or letters that are language-specific and non-international. In Denmark for example, we have letters like Æ, Ø, and Å which others don’t and URLs are unable to have any of these.
Use hyphens: To separate words in the URL, it’s best to use hyphens (“-“) instead of underscores or spaces. This improves the readability and comprehension of the URL. Google reads hyphens as spaces.
Page titles and meta descriptions (metadata)
As a beginner in SEO, it can be difficult to navigate the meaning of words because there are many words for the same thing. This is the case with page titles and meta descriptions, also known collectively as metadata.
Metadata are elements you find in your site’s code – and don’t worry, you don’t have to dig into the code to optimize either page titles or meta descriptions.
The page title is the text that appears in your browser tab and is also the text that appears when you look at the Google search engine results page (also known as “SERP”) as illustrated in the image below. The meta description is the longer description (in black) below the page title.
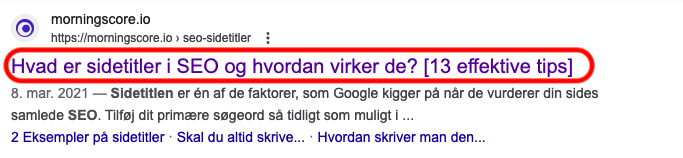
All your titles and descriptions should be unique and thus not duplicated, contain the primary keyword that you are trying to rank for (preferably as early as possible in the sentence), and be neither too long nor too short.
Both metadata are important for your SEO work. The page title has a direct impact on your rankings on Google. In addition, it has a big impact on your click-through rate (what percentage of people who see your page in the search results end up clicking on your page), because a well-written and interesting page title will make people click on your page rather than your competitors.
The meta description is also important, but not quite as important as the page title. The meta description doesn’t have a direct impact on your rankings, but can positively and negatively affect your click-through rate depending on how well-written and interesting it is.
Beginner tip: Make your page titles between 20-70 characters and your meta descriptions between 120-160 characters.
Headline optimization (H1, H2 and H3)
A well-structured page with proper use of headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.) also known as “H-tags” not only helps users understand your content but also search engines understand the hierarchy of information on your page.
All your landing pages should have headings, but it doesn’t matter what the headings are. They should be optimized for the keyword(s) you want to rank for on your blog posts, category pages, and product pages.
Overall, there is only one guideline that is a must: Have only one H1 per landing page.
H1 – Your overall/primary headline that you only use once.
H2 – Subheadings for section divisions
H3 – Sub-subheadings for paragraphs within paragraphs. Used when you go a little deeper into a topic.
H4, H5, and H6 – For unimportant headings or highlighted details. Rarely used for anything other than enlarging parts of texts without the use of custom code.
Here it’s important to go back to your keyword analysis and use your primary and secondary keywords hierarchically according to how important they are to you.
For the remainder of your H2s and H3s, it’s “free play”, but make sure they are relevant to the topic and if possible, include related words (also known as LSI keywords) in your remaining headings to stay in the “universe” and provide additional context.
Beginner tip: Use your primary keyword in about 70% of your headlines.
Describe your images with alt tags
Alt tags are also known as alt text, alternative text, and a lot of other things that make it a little harder for SEOs to get their heads around.
Alt tags are small tags in the code where you have the option to describe what’s in an image. It creates context and helps Google understand what’s in an image to assess how relevant the image is to the context of your written content. In other words: image SEO.

The most common way to add alt tags to images is via your CMS’s media library, so you don’t have to mess with the code here either.
In addition, alt tags are the text that blind people can read out and explain what’s in the images on your page.
When you hover your mouse over an image on a website, a text appears. This is not an alt tag. It is the title text for the image and is not the same.
An alt tag should be written in a complete sentence and should not be written in bullet points or abbreviations. Write a complete sentence that explains what’s in the image. If you can use your keywords in the text in a natural way, it’s a plus and increases your chances of being found on image searches on Google.
Beginner tip: Make the file name as appropriate as possible for what’s on it and use only hyphens (-) and not underscores (_)
Internal links – create optimal navigation
Adding internal links between your different pages helps search engines understand the context of the content on your website and navigate them between pages.
In addition, it significantly increases user-friendliness because they are also navigated to relevant pages. This benefits you in several ways, as your users stay on your website for longer, read more of your content and see more of your products. All elements that increase the likelihood of them making a purchase.
It’s important that you don’t overuse internal links. Use internal links when it creates value for your users in the same way that in this post, which is written for beginners in SEO, I link to other relevant pages throughout the post to direct you to pages where you can read more about the specific topic being written about or in connection with words that you may/may not know about as a beginner.
In this post, I use internal links to our other resources that go more in-depth on each topic. This way, I create value for you if you want more knowledge about the topics – it’s rewarding for a post about SEO for beginners because you are now in a learning phase and I want to give you all the information you need to go from having basic knowledge about SEO to having broad knowledge about SEO.
Example:
If you’ve written a blog post about dog food, you’ve probably written about what types of dog food there are, what’s good for different dogs, and what quantities are suitable for different dog sizes or breeds.
Here you can create another blog post about what a dog shouldn’t eat and link from one page to the other.
It’s super relevant to users and Google will reward you for it.
Beginner tip: Make the link on the word you’ve targeted on the page the link leads to. This is also called “anchor text”.
Create consistency in your OnPage SEO
You’re well on your way to having your site search engine optimized if you make sure they follow a common thread throughout the site:
- Page titles
- H1, H2 and H3 headings
- Texts
- Metadata
- Internal links
- URLs
- Structure/navigation
- Images and videos (descriptions)
- Structured data (Schema)
Make sure to use your primary keyword in all of the above elements and you’ll already be ahead of the game. Use an SEO checker to point out any OnPage issues to fix.
Off Page SEO for beginners

Off-page SEO is all the actions performed outside of the website itself to improve its visibility and ranking in search results.
It focuses on building a strong online presence and authority by, among other things, getting other websites to link to your own site and engaging with users on different platforms. Off-page SEO is crucial because search engines, especially Google, consider inbound backlinks and online mentions as a sign that a site is valuable and trustworthy.
Link building for beginners
Speaking of search engine optimization, link building is an important strategy that all website owners should focus on.
Link building is a practice where you actively work to get links from other websites to your own website. These links act as “votes” for your site, as search engines see them as recommendations or proof that your content is valuable and trustworthy.
When other websites link to you, it signals that your website is authoritative and relevant, which can improve your ranking in search results.
Link building is important for SEO because:
- It increases your visibility: When your website has more quality links, it has a greater chance of ranking higher in search results.
- It generates traffic: Links from other websites act as traffic channels to your website if they are relevant. When users click on these links, they are directed to your site, increasing your organic traffic.
- It builds authority: Quality links from credible sites build your website’s authority in the eyes of search engines. With higher authority comes higher rankings on Google.
- It helps get pages indexed: Search engines use links to find and index new pages on your website. The more links you have, the faster your pages will be discovered and indexed.
“How to get links” for beginners:
- Good content: Create original, valuable, informative, and shareable content that other websites will be interested in linking to.
- Guest posts: Contribute guest posts on relevant blogs and websites to build relationships and get links. It requires an active effort to find relevant sites and, most importantly, to contact the owner and offer them a high-quality and relevant post for their users in exchange for a link to your website in the post.
- Linkbait: Create content that is so good that others will naturally link to it, such as infographics, guides, or interesting articles.
- Collaboration: Collaborate with other businesses and organizations to exchange links and boost
- each other’s visibility. This can be in collaboration with partners, suppliers, and the like.
Beginner tip: As a Morningscore customer, you get access to lists of free Danish and international link opportunities.
Local SEO – the goldmine for service businesses

Local SEO is an SEO strategy that focuses on improving the visibility and reach of a business or physical store on the internet within a specific geographic area. The goal of local SEO is to get your business to rank high in local search results when potential customers search for products or services in their local area or use geographical phrases directly in their search, for example by searching: product/service + city (Hairdresser in Odense).
Local SEO is particularly relevant for service businesses, but can also be relevant for product sales.
Working with locally targeted SEO includes:
Google Business Profile (formerly Google My Business): Creating and optimizing your Google Business profile is essential for local SEO. Google Business is a free service from Google where you can display information about your business, including opening hours, address, phone number, reviews, and images. This makes it easier for potential customers to find and contact you.
NAP consistency: Name, address, and phone number (NAP) should be consistent across all online platforms, including your own website, social media, online directories, and review sites. Consistent information helps search engines validate your business and improve your local search rankings.
Local keywords: Use relevant keywords that include city name or locality in your content and metadata. This signals to search engines that your business is relevant to local users because you build the context that your business operates and is relevant to a specific geographic area.
Online reviews: Positive reviews from satisfied customers have a big impact on your local credibility. Encourage your customers to leave reviews on your Google Business profile and other important review sites.
Local backlinks: Get links from other local businesses, organizations, and local news media. Local backlinks strengthen your local authority.
Measuring and analyzing SEO results
Measuring and analyzing SEO results is essential to understand how your website is performing in search engines and to identify areas for improvement. Here’s a simple guide on what to look for and how to do it (NB. SEO analysis can be much more complicated and in-depth, but because this post is for beginners in SEO, it’s basic analysis):
- Keyword rankings: Check how well your most important keywords rank in search results. Use SEO tools with a rank tracker like Morningscore and/or Google Search Console to see the rankings of your keywords.
- Organic traffic: Measure how many visitors you get from search engines. Google Analytics (GA4) is a useful tool to track the traffic to your website and analyze its source.
- Click-through rate (CTR): CTR is the percentage between the number of clicks on your search result and the number of impressions. Analyze which keywords and meta titles have a high CTR as it can indicate that they are relevant and appealing to users.
- Bounce rate: Bounce rate is the percentage of visitors who leave your site after visiting only one page. A low bounce rate is usually better as it shows that users find your content relevant and click further around your site.
- Conversions: Identify how many visitors perform a desired action on your site, such as filling out a form or buying a product. Conversions of one kind or another can be tracked with Google Analytics and others, but it requires some setup.
- Backlinks: See how many external websites are linking to your website and where these links are coming from. Assess the quality of these links as they affect your website’s authority.
- Keyword traffic: Find out which keywords drive traffic to your website and if you need to optimize your content for more relevant keywords.
- Content analysis: Evaluate which content performs best. Identify popular posts and consider creating more similar content.
To make measurement and analysis easier, it’s recommended to use one or more SEO tools such as Morningscore, Google Analytics, Google Search Console and SEO Site Checkup. These tools give you a comprehensive insight into your website’s performance and help you make informed decisions on how to improve your SEO efforts. Morningscore offers a simple SEO reporting tool which makes you able to create ongoing automatic reports about your SEO performance.
Remember to measure and analyze regularly, as SEO is a continuous process that requires constant monitoring and adjustment.
Avoid common SEO mistakes as a beginner

When it comes to SEO, there are a number of common mistakes to avoid that are easy to fall into as a beginner. Here are some of the most common mistakes:
- Over-optimizing keywords: Using too many keywords in your content can lead to it appearing artificial and spammy. It’s important to use keywords naturally and make sure the content is still readable and valuable to users. Avoid keyword stuffing and adding your keyword over and over again in an attempt to manipulate search engines.
- Ignoring mobile optimization: With the increasing use of mobile devices, having a mobile-friendly website is crucial. Ignoring mobile optimization can lead to a poor user experience, which can negatively impact your ranking in search results.
- Poor quality content: The content on your website should be informative, relevant, and unique. Poorly written or copied content will not get you to the top. Duplicate/copied content is directly against Google’s guidelines and will negatively affect your rankings.
- Failure to use internal links: Internal links help connect different pages on your website and give users easy access to relevant information. If you don’t use internal links, you’re missing out on some of the “easy” points and the opportunity to pass value between your pages.
- Ignoring backlink quality: Having a lot of backlinks is good, but it’s important to focus on the quality of those links. If you only have a lot of SPAM links from suspicious Chinese and Russian websites, your links are worthless. Go for links from Danish websites that have some relevance to your niche.
- Under-prioritizing technical SEO: Technical aspects of SEO, such as fast loading time, correct URL structure, and proper XML sitemap, are important for a successful SEO strategy. Not prioritizing technical aspects can slow down your website and affect its visibility in search engines.
- Ignoring analytics: Monitoring and analyzing your website’s performance is crucial to understanding which SEO measures are working and which need improvement. Ignoring analytics can lead to missing out on important insights that can help you optimize your SEO efforts.
SEO tools for beginners
By the time you get to this point, you’ve gone from being a beginner to having a really strong understanding of what SEO is and how to approach it. Before you get started, it’s important that you know which SEO tools you need to use. We’ve compiled a larger list of the best SEO tools, but here’s our recommendation for the best tools for beginners:
- Morningscore (Find keywords, track keywords, track links, website health, guides, keyword analysis)
- Answer The Public (Get ideas for keywords and questions)
- Woorank (Track keywords, health and reporting)
- SEO Site Checkup (health check)
- Google Search Console (Traffic data, click-through rate, impressions, existing keywords)
- Google PageSpeed Insights (Load speed optimization)
- Yoast (Plugin)
- RankMath (Plugin)
Beginner tip: Don’t use just 1 tool. Several of the above are free and can be used alongside each other for different functions.
Conclusion
In this post, we have covered the basic principles of SEO for beginners. We have learned that search engine optimization is a crucial discipline to improve the visibility and rankings of our website in search engines. For beginners, it’s important to remember that SEO is a continuous process that requires patience and persistence – so be careful not to give up too soon.
We’ve looked at important aspects of SEO, such as keyword analysis and research, where it’s crucial to find relevant and business-critical keywords that match the search behavior of our target audience. Then we focused on on-page SEO, where we looked at optimizing content, meta tags, URL structure, and internal links to make our websites more interesting for both search engines and visitors.
In addition, we’ve looked at the importance of off-page SEO, where we need to build quality links to build authority and trust in our website. We have also touched on the importance of technical SEO, where it is crucial to make sure that our website is technically sound and user-friendly.
By implementing the basic SEO principles, beginners can build a solid foundation to improve website visibility and increase organic traffic.
Remember, SEO is a continuous process and it’s important to stay up-to-date with the latest changes in search engine algorithms.
So get started with SEO, be persistent, and achieve the highest rankings. Best of luck to you!
Beginners in SEO often ask:

What is SEO?
SEO stands for “Search Engine Optimization”. It is a process of improving your website’s visibility on search engines such as Google, Bing, and Yahoo. The aim is to drive more organic traffic to your website and improve its ranking in search results.
Is SEO a one-off task or continuous work?
SEO is a continuous process. Search engine algorithms are constantly changing and the competition for rankings in search results is also changing. Therefore, SEO requires regular attention and maintenance to maintain and improve your website’s ranking in search results. Competitors may also be working to improve their SEO, which can affect your ranking if you don’t keep up. Therefore, SEO should be seen as a long-term investment in your website’s success.
Why is SEO important?
SEO is important because most people, including your potential customers, use search engines to find information, products and services online. If your website is not search engine optimized, it can be overlooked and you will miss out on potential visitors and customers.
What is the difference between organic traffic and paid traffic?
Organic traffic comes from search results where people click on your website because it appears relevant to their search. Paid traffic comes from ads (typically the top 2-4 results marked “ad”), where you pay to have your website appear at the top of the search results (pay per click (CPC)).
How do search engines work?
Search engines use complex algorithms to analyze websites and rank them in search results. They evaluate factors such as relevance, user experience, quality of content and links to the website.
When do I start seeing results from my SEO efforts?
It can vary, but it usually takes time to achieve visible results. Some SEO changes can have a quick impact, while others can take weeks or months to manifest. Be patient and persistent and don’t get discouraged if you don’t see big results after a few weeks – it’s perfectly normal.

