On Page SEO is the one part of SEO with the biggest impact as even small changes can have big impact on your rankings and organic traffic.
Basically, On Page SEO factors are decisive if you make or break your SEO strategy.
At the same time, On Page SEO is the easiest and most accessible part of SEO for beginners, and don’t require any special knowledge that you can’t learn by yourself – in contrast to technical SEO which requires a certain skill set and technical know-how.
Reading this post you are either just starting to learn about SEO or facing ranking issues even though you have optimized the hell out of your pages.
Say no more. No matter the reason you read this, I will make sure that you know everything about On Page SEO and are fully capable of optimizing your landing pages.
With 7 years of experience within SEO I have been in touch with a ton of SEO cases focusing primarily on Onsite and content optimization. I’ll provide you with everything you need to be able to create landing pages that Google love and praise.
What is On Page SEO?

On Page SEO is all of the optimization on your website that makes search engines as well as users love your pages. The classic On Page SEO factors are known as optimizing titles, content, URLs and internal links.
On page SEO, also known as on-site SEO, is the process of optimizing individual web pages to improve their search engine rankings and attract organic traffic. This involves tweaking various elements within your control, such as content, HTML source code, meta tags (title tags and meta descriptions), and images. The goal is to ensure that your pages are both user-friendly and search engine-friendly.
In addition to that, On Page SEO is about creating appealing websites that provides original and helpful content and displays expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness and most important that your page matches the search intent from the user.
On page SEO is like setting the stage for your website’s big performance. It’s all about fine-tuning the elements that Google and other search engines love.
Imagine it as sprucing up your living room before guests arrive – you tweak the lighting (title tags), fluff the cushions (meta descriptions), and as a top host ensure the conversation flows naturally (high-quality content).
The aim? Make your site as inviting as a warm cup of cocoa on a rainy day. This means using keywords thoughtfully, crafting engaging and informative content, and ensuring your site is a breeze to navigate.
Think of it as giving your site a bit of a makeover – it’s not just about looking good, but feeling good too.
What is the difference between On Page SEO and Off Page SEO?

The difference is that On Page SEO is all the elements that you have control of and are all the things you can do internally on your pages.
In contrast, Off Page SEO is all of the external factors that affects your search engine rankings that you can optimize.
Backlinks, social media signals, media coverage, etc are all external factors that you can push for to boost your rankings but that you can’t do anything about internally on your website.
Why is On Page SEO important?
On Page SEO is vital to any successful SEO case as content are what search engines understands and connects user with.
All the On Page factors helps crawlers read and understand your content and the context as well as matching relevant results to the searchers query.
Let’s break down the On Page SEO factors and why each is important:
- Relevance and visibility: Proper on page SEO techniques help search engines understand the content of your webpage, which improves its chances of ranking higher in relevant search queries. This means more visibility and potential traffic to your site.
- User experience: Optimizing on page elements like title tags, meta descriptions, headings, and content structure creates better user experience. When users find your site easy to navigate and information-rich, they are more likely to stay longer and engage with your content.
- Targeted traffic: By optimizing for specific keywords and phrases that your target audience is searching for, on page SEO helps attract visitors who are likely interested in your products, services, or content.
- Crawlability and indexability: Search engines use crawlers to scan and index web pages. Proper on page SEO ensures that these crawlers can easily interpret your content, improving your site’s chances of being properly indexed.
- Competitive edge: In competitive industries, effective on page SEO can differentiate your site from others. It can help you outrank competitors who may not be as optimized, thereby capturing more traffic and potential customers.
- Cost effective: Compared to off page SEO (like link building), on page SEO is generally more within your control and doesn’t necessarily require ongoing expenses. It’s about creating quality content and optimizing it properly, which can yield long-term benefits.
- Foundation for Off Page SEO: On-page SEO forms the foundation upon which other SEO efforts are built. For instance, quality content that is well-optimized is more likely to attract backlinks naturally, which is beneficial for off-page SEO.
Google continues to evolve its algorithm but what never changes is the importance of content and user experience.
As Google changes the algorithm to be more and more user-centric your On Page SEO is more important now than ever.
Valuable, original and helpful content is the winner when it comes to ranking on Google.
So, how do you do On Page SEO then?
Let’s break down what you need to do to make Google love your pages.
How to do On Page SEO
This how-to is very important as there is a lot of outdated and wrong information out there about this.
On Page SEO have changed a lot since 5-10 years ago but many SEOs keeps preaching 2010 SEO advice.
Back in the old SEO days On Page SEO was fairly easy.
To do On Page SEO years ago you simply wanted to make sure that you had a keyword density high enough on a page and add it to all headers.
Luckily for both SEOs and especially users this have changes to be much more comprehensive with a bigger focus on user intent and content quality.
Let’s dig into the On Page ranking factors and what to optimize onsite.
Finding relevant keywords
The very first step os to do proper keyword research to find the right keywords that the users search for to find your product or service to know what to optimize your content and other onsite factors for.
To conduct thorough keyword research you need a keyword research tool as Morningscores, search for potential keywords on Google to see the results and add the ranking competitors to your SEO tool to see what they are ranking for that could be relevant for you to target.
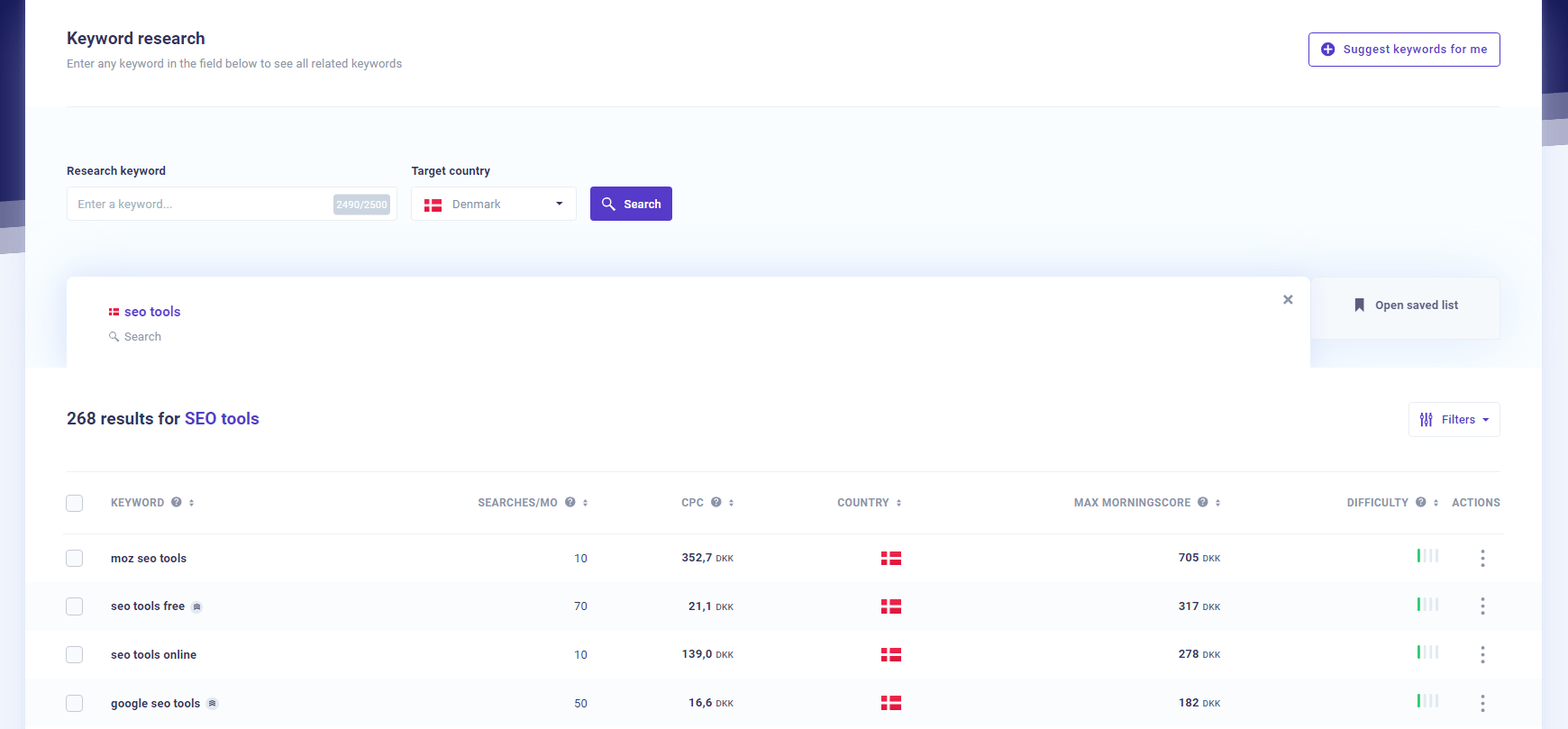
Conducting keyword research is not only finding keywords that people use when they are ready to buy.
You need to find keywords and create landing pages and content that cover the full buyer journey and be visible in the top funnel, mid funnel and bottom funnel and satisfy the different queries search intent.
Buyer journey stages explained
- Awareness (top funnel): To target users in the awareness phase you need to provide high quality and helpful blog posts, videos or a proper homepage with info.
- Consideration (mid funnel): Targeting users in the consideration phase is important because this is right before they buy a product – they just need to be fully convinced by your case studies, a good about page, buyers guide, etc.
- Decision (bottom funnel): Users are ready to buy and you need landing pages that are optimized for this. Provide product demos, comparisons, clear pricing pages and contact forms and/or simple contact pages.
When you have your keywords figured out and listed in your rank tracker it’s time to optimize your webpages.
Understanding search intent and satisfying users
In the wild, wild west of SEO, there’s a sheriff in town: Search Intent. And, trust me, this sheriff doesn’t play around.
Understanding search intent is like having a treasure map that leads you to the gold—SEO gold, that is.
But before I get carried away with metaphors, let’s dive into what search intent really means and how you can use it to make your users (and Google) smile.
What Is search intent?
Search intent, also known as user intent, is the purpose behind a user’s search query. It’s the “why” behind the words they type into the Google search bar.
Are they looking to buy something, learn something, or find a specific website?
Understanding this can make or break your content strategy.
Imagine you’re throwing a party. You wouldn’t serve lasagna if everyone’s expecting sushi, right?
The same goes for your website content. You need to serve exactly what your audience is craving, or leave them disappointed and fall down the Google-ladder.
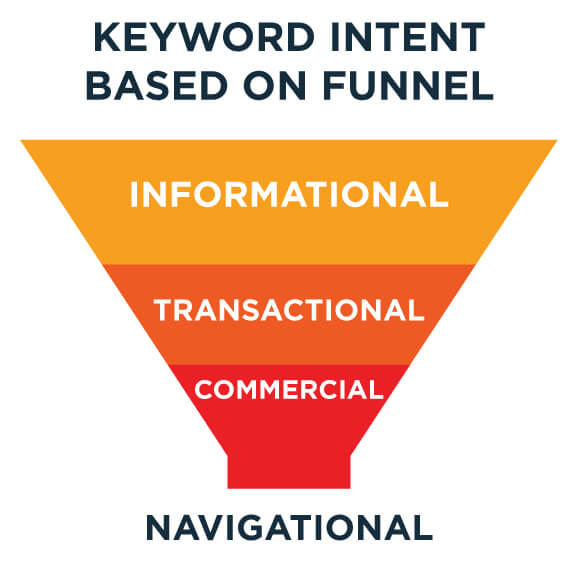
Types of search intent
There are generally four types of search intent. Let’s break them down:
- Informational intent: The user is looking for information. They might ask, “How do I bake a cake?” or “What is search intent?”. These users are in research mode. To rank for that keyword you need a blog post answering that question and possibly other relevant follow-up questions to be relevant.
- Navigational intent: The user wants to go to a specific site. For example, “Facebook login” or “Nike website”. They know where they want to go, and they’re using Google as their map. Keywords with this intention is irrelevant for any other business that is not the company or website mentioned in the query.
- Transactional intent: These users are ready to buy. They might search for “buy iPhone 13” or “best deals on laptops”. They’ve got their wallets out and are ready to make a purchase. Depending on how concrete they mention a product you want to create or optimize your product page or category page. Optimize product pages for exact product names only.
- Commercial investigation: This is a mix of informational and transactional. Users are researching before making a purchase. Queries could include “best smartphone 2024” or “iPhone 13 vs Samsung Galaxy S21”. Queries like these requires you to create a comparison landing page titled “the 10 best smartphones in 2024” or similar, create a list with comprehensive and objective descriptions of each and everyone, conclude with pros and cons for each and the price (remember to link to your product if you are also a retailer).
Why is search intent important?

Understanding search intent can’t be underestimated because it aligns your content with what users are actually looking for.
This means better user satisfaction, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates. Plus, Google loves it when you make their users happy and rewards you with better rankings.
Google is focusing more and more on the search intent to connect users with the best available results.
Hence, you are required to create blog posts, category pages, product pages, guides, comparisons and much more to target all search intents and user needs.
How to determine search intent
Figuring out search intent can feel like detective work. Here’s a magnifying glass for you:
- Look at the keywords: Some keywords scream their intent. “Buy,” “best,” “how to,” and “reviews” are pretty telling.
- Analyze the SERPs: Check out what’s ranking on the first page for your target keywords. If you see a lot of product pages, it’s likely transactional. If it’s blog posts and guides, it’s informational.
- Use SEO tools: SEO tools can provide insights into keyword intent.
Creating content that satisfies user intent
Alright, you’ve cracked the case. Now, how do you create content that hits the bullseye?
- Match content type to intent: If the intent is informational, create blog posts, guides, or videos. For transactional intent, focus on product pages, reviews, and comparisons.
- Answer the question: Get to the point quickly. If someone’s asking “how to bake a cake,” don’t start with the history of cakes. Give them the recipe, and maybe toss in a fun fact or two. After you have provided the clear answer you can go on about other related information.
- Provide value: Go beyond the basics. Add unique insights, data, or tips that your competitors might not have. This not only satisfies the user but also establishes you as an authority.
- Optimize for readability: Use short paragraphs, bullet points, and subheadings. Make your content easy to scan for the human eye.
- Include multimedia: Images, videos, infographics—all these can enhance the user experience and keep them engaged. .
Let’s not forget that the web can be a pretty boring place sometimes. Adding a bit of personality into your content can make it more relatable and enjoyable.
After all, people connects with people and when you are unable to see people in real life, you need to make your content personally.
Understanding and fulfilling search intent is the secret sauce of successful On Page SEO.
It’s about putting yourself in your user’s shoes and asking, “What are they really looking for?” When you get this right, you’re not just playing the SEO game—you’re winning it.
So go ahead, dive into the minds of your users, and give them exactly what they’re looking for. And maybe throw in a cat story or two.
Create engaging title tags
The page title is the large text (title) you see for the results in the search engine result page.
In the title shown in the image below, we have a title with the keyword “SEO to CPC translator” as the main keyword as the first thing.
Next, we add more context and something of interest to make the user click by writing “see the real value of your keywords” which is both a semantic keyword to the main keyword but also speaks directly to what the user is looking for when searching for an SEO to CPC translator.
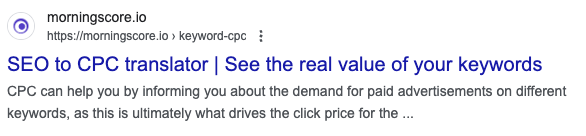
The page title is one of the single most important elements of the On Page SEO. No factors can stand alone though.
The purpose of the title is to clarify for search engines and users what to expect on the corresponding landing page and summarize the page of the content – don’t oversell it.
The title tag is also where you can make sure to match the searchers intent by adding your keyword to it.
- Place your main keyword first in the title or as early as possible.
- Incorporate the keyword in a natural way and use 1-2 full sentences that makes sense and creates interest for the searcher to attract the click.
- Make sure to keep the title below 70 characters to avoid it being truncated by Google or completely re-written.
- Include year, numbers or other data if relevant for the subject
ℹ️ Continue reading about title tags.
Publish high quality, helpful and original content
Recent years Google have developed in a direction that focus on quality, originality, and level of helpfulness.
SEO content is not just adding keywords everywhere anymore. You have to provide real value, information and cover subjects comprehensively and most important of all that your content matches the search intent and provide either new information on the subject instead of reciting existing sources or provide more clear, easier understandable information.
Focus on the following things to create user-centric and helpful SEO content:
- Focus on people-first content: Prioritize creating content that addresses the needs, questions, and interests of your target audience. Make your content valuable, informative, and relevant to the user’s search intent. For informational searches you won’t rank with your category pages. To rank for informational searches you need to provide relevant information.
- Incorporate E-E-A-T principles: Boost your content’s Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) by providing accurate information, citing reputable sources, and demonstrating your expertise on the subject matter.
- Use clear and engaging headlines: Craft headlines that are clear, compelling, and accurately reflect the content of your page. A strong headline can significantly improve click-through rates and user engagement. On top of that, point out your skillset and experience and background in order to gain trust and authority and link to your about page with your results and experience.
- Answer user questions thoroughly: Identify common questions and concerns of your audience and address them comprehensively in your content. This can be achieved through keyword research and understanding user intent. Cover subjects from A-Z using the topic cluster strategy.
- Maintain originality: Create unique content and offer a fresh perspective or additional insights compared to existing content. Avoid duplicating content from other sources to maintain originality and SEO performance. The top ranking websites are the best sources of inspiration and to know what content you need to cover to be relevant – you just need to do better.
High quality webpages
High quality content is defined as serving a beneficial purpose and achieving that purpose throughout the content.
A beneficial purpose can be a wide range of things and is everything from providing new, original information, selling products or even creating funny things that makes people smile.
To determine if you have created high quality content you should consider:
- The purpose: Do your page have a beneficial purpose? Does anyone get anything out of this page?
- Potential to cause harm: If your page have the potential to cause harm your page will not be high quality.
- Page topic and type of website: Do the topic of the page match the general topic for the website? If you run a webshop or YMYL-site (Your Money or Your Life) you should be extra thorough.
- Page title: High quality pages include a well crafted page title that summarize the page and isn’t sensational. If you over sell or under sell the page in the title it can be considered low quality.
- Ads: Are your page covered in ads? Do ads interfere with the page, structure or content? You can monetize your traffic from ads but if they interfere or block your content it will be considered low quality.
- Information from website and creator: Do the page include enough information about the website and the creator of the content?
Next element to be addressed to determine if the page can be considered high quality. At least one of the following 3 elements should be applicable on your page to be considered high quality:
- Content quality: Content crafted with a lot of effort (thorough), a high level of originality or skill so the content matches and achieves the purpose.
- Reputation: The website has a reputation within the topic for the page as well as the content creator (person) has a reputation for the subject.
- Trust: The page addresses and provide a high level of Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness regarding the purpose of the page.
Provide a high level of E-E-A-T

E-E-A-T factors are not equally important for any website or webpage. The need of E-E-A-T depends on the purpose of a webpage or topic.
A high level of Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust can be necessary for a webpage or a topic to be able to achieve the purpose of the page.
E-E-A-T explained
- Experience: It’s positive for all websites and all topics (but not necessary per se). First hand experiences with a product, knowledge or anything else is high quality of experience hence social media, forums, etc. will often have a high quality of experience because of real people is sharing first hand experiences with something. To reach a high level of experience for your webpages you can add personal experiences, personal opinions or similar to the content within the topic for the page.
- Expertise: It is required for a wide range of different topics and webpages (some more important than others). Lawyers, photographers, accountants requires a high level of expertise to provide trustworthy content as it requires a certain skill og knowledge which they have to address in the content. Expertise is not only applicable for highly specialized topics as the previously mentioned but are also valuable for anyone else from hobby-sites to news-sites.
- Authority: Any type of page and any type of content can get value from being authoritative. The government tax authority is a go-to source for tax information, forms, etc. while a local business can be an authority as the go-to website for local information. Authority is not a fixed factor but it depends on the type of business and the topic.
- Trust: Trust is valuable for all types of websites but is especially crucial for the YMYL-websites such as financial services. For non-YMYL websites not covering YMYL-topics you can increase the level of trustworthiness by getting company reviews, product reviews. Trust is not make or break for all but it is valuable.
Use and optimize headers and structure
Headers are important to build structure, break up your content in easier, smaller and skimmable pieces.
Your headline should immediately convey the main benefit or value proposition of your page to attract and engage visitors.
Additionally, a logical header structure help Googles crawlers understand the content and index your page.
To help Google understand the content and match users search intent add the primary keyword to your H1, 60-70% of your H2’s and H3’s and use headers with semantic latent (related) keywords.
Thumb rules to follow:
- Use only 1 H1 on every landing page
- Use H2’s as many times as the topic requires
- Use H2’s for the main subjects of the page
- Use H3’s for further information connected to the points in your H2’s
- Never skip a header. Create a logical hierarchy and have an H2 after the H1 followed by an additional H2 or H3 – never go straight to H4 unless the previous header was H3.
Subheaders will create a better user experience by improving readability, skimmability and ultimate easier to understand for users as well as search engines.
Place main keyword in vital elements
Google is still all about content and to appear as a relevant result for user queries you need to make the content relevant for it.
Google will scan your content and mathematically evaluate the content quality and relevance.
Add your primary keyword strategically throughout your content – but only when it fits the purpose and sentence.
Add your main keyword to:
- H1
- Page title
- First paragraph within the first 100 words
- Subheaders
- Image alt text

Placing your keyword in crucial on page elements is to create context and make it easy to understand for search engines what the context of the content is.
To further create context about the subject you need to add variations of the keyword as well as using semantic words to cover the subject and help Google understand the content.
Semantic keywords are words related to the topic.
For example:
Semantic related keywords for “swimsuit” is pool, beach, summer, sun, bathing and similar words that relates to swimsuit or the use of a swimsuit.
Add internal links in your content
Internal links are links from one of your webpages to another one of your own webpages. See below how an internal link looks on a webpage:

Internal links are another important – yet often under prioritized – on page SEO factor.
Internal links help search engines as well as users understand the structure of the website and guides crawlers around your website to discover and index new pages.
On top of that, internal links helps Google understand how your webpages relates to each other and sends signals to Google that the linked page is a valuable page.
Time spent on site is an on page SEO factor and internal links also guides users around to other pages making them spend more time on your website.
Adding internal links on keyword anchors will help Google understand the context of the linked page and is a way to work around potential cannibalization issues by showing Google what pages are the recommended page for the keyword.
ℹ️ Continue reading about internal links.
Add external links
In contrast to internal links external links are links from your webpage to a webpage on another domain.
External links help you increase authority of you page by linking to authoritative sources.
This is an often overlooked SEO factor as many SEOs have been misunderstanding the concept for years and referring to external links as something that takes value from your page and passes to the linked page.
That is not correct.
Linking to trustworthy and authoritative sources is helpful for the user and builds trust in your content.
Adding external links can have a negative effect though:
- Link only to relevant, authoritative and trustworthy content.
- Add a descriptive anchor to summarize what search engines and users are being linked to
- Avoid stuffing your pages with external links
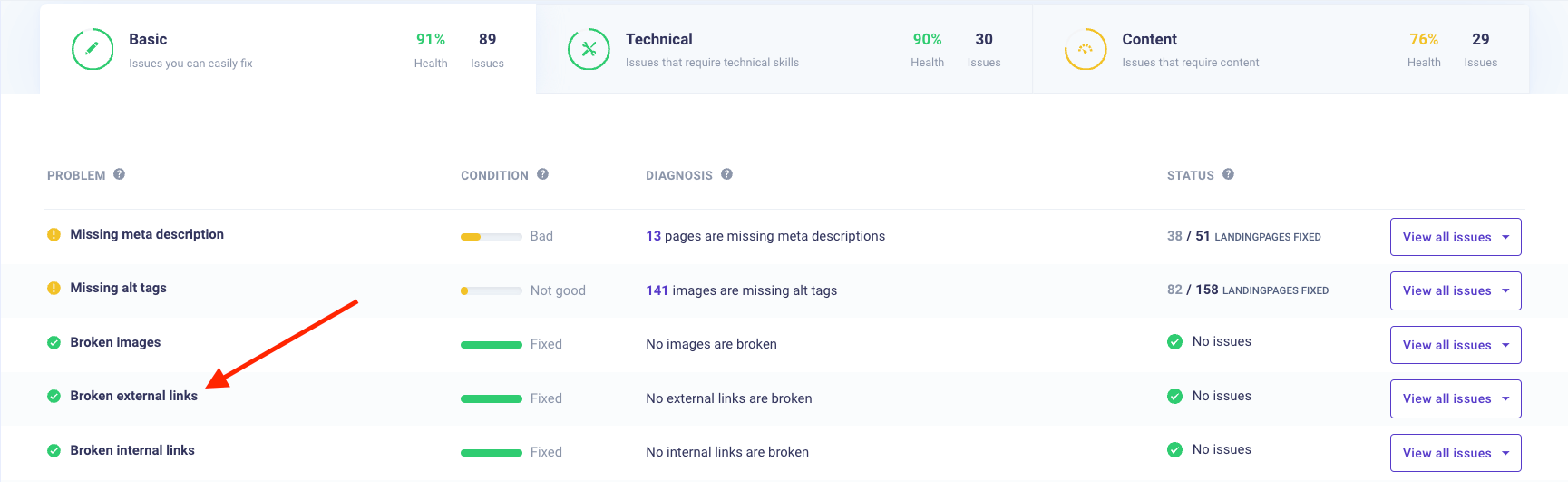
Check if you have issues with external links with our broken link checker.
Simply go to “health” and the tab “basic” and find issues regarding broken external links.
Add and optimize images
Images, videos, infographics and other multimedia elements increases user experience on your page which you know from earlier in this post is an important part of on page SEO.
Additionally, including images in your content will increase the chance of achieving visibility in Google Image Search and generate more organic traffic.
First of all, you need to add a descriptive alt tag to the image and add the main keyword. Check if you have images without alt tag here.
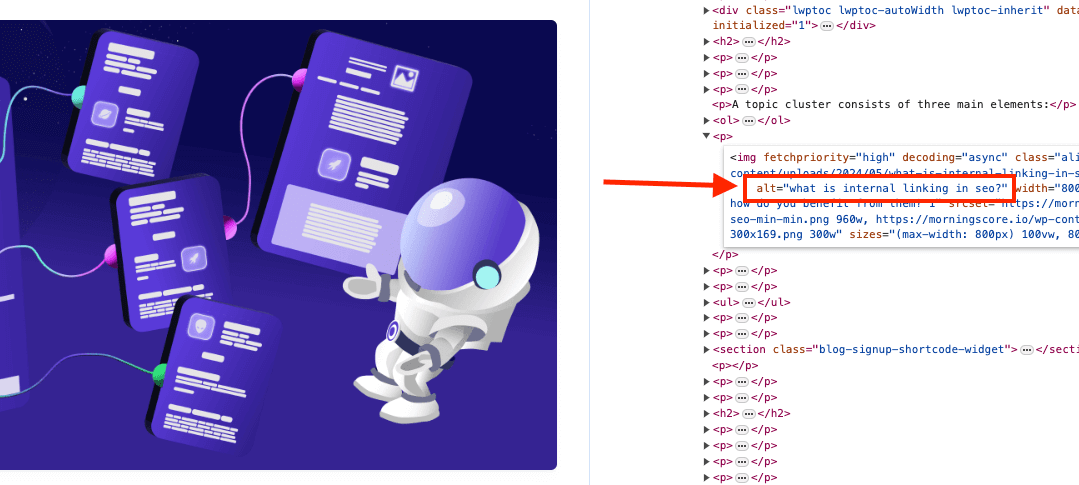
Alt tag serves multiple purposes but originally they were meant for screen readers to read up the image description for vision-disabled people.
Today, they still serve that purpose but they also adds context for search engine crawlers making them understand what is on an image and understand the relation to the content.
Alt tags are an HTML element and it looks like this in the page code:
Craft appealing meta descriptions
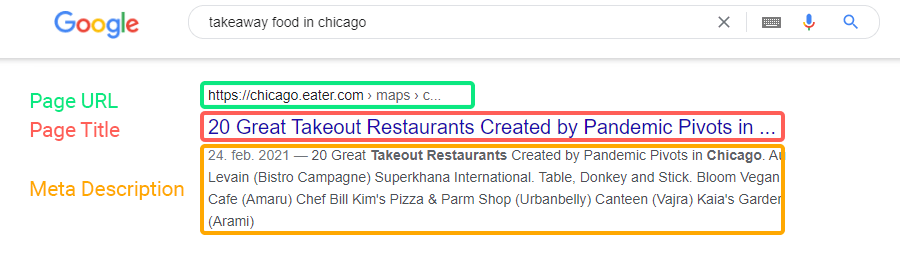
A meta description is an HTML element that provides a brief summary of a web page’s content.
This snippet of text is displayed as part of the search engine results page below the page’s URL and title.
Meta descriptions serve to inform and interest users with a short, relevant summary, acting like a pitch to encourage clicks from search results.
Meta descriptions are an essential part of on page SEO, as they help describe the page’s content and can influence click-through rates (CTR) by providing potential visitors with a snapshot of what to expect on the page.
Meta descriptions don’t have influence on your Google rankings.
Not directly at least.
The meta description can be what convinces the user to visit your page instead of a competitor webpage. A higher click through rate can affect your rankings so do not forget to give a little bit of love to the meta descriptions.
Follow these guidelines for creating meta descriptions:
- Keep the meta description shorter than 120 characters. Search results on mobile devices have less space available and meta descriptions longer than 120 characters will be cut off for mobile users.
- Include the main keyword to achieve part of your description to turn bold. This will show users as well as search engines that you are a match for the users query.
- Add call to action and give users a reason to click. Convince the user – without lying about what they can expect – by adding “read more”, “learn the framework” or “try free”.
Check if you have too long or too short meta descriptions here.
SEO friendly URLs
An SEO-friendly URL is a web address designed to meet the needs of both users and search engines. SEO-friendly URLs are structured to be easily readable and relevant to the content of the web page, helping search engines understand what the page is about and providing a better user experience.

What does Google themselves say about it?
Google emphasizes the importance of a clear, logical URL structure. They recommend using descriptive URLs that include keywords, as keywords help search engines understand the content and context of the pages better.
What to consider when creating URLs?
- Describe your content: Use words that clearly describe the page’s content but keep it short.
- Include keywords: Add relevant keywords that reflect the content of the page.
- Use hyphens to separate words: Hyphens improve readability for both users and search engines. Avoid using underscores. Hyphens are officially the space separator for Google.
- Use lowercase letters: Use lowercase letters helps maintain consistency.
- Keep it simple and short: Shorter URLs are easier to read and remember. Avoid unnecessary words and parameters.
- Standardize URL naming conventions: Consistency helps in maintaining the URL structure clean and easy understandable.
- Limit URL length: There is no golden rule here but a user-friendly is a URL that is easy to remember. The longer it is and the more parameters it has the harder it is to remember.
SEO-friendly URLs are important because they improve the user experience and help search engines better understand your website’s structure and content. A well-structured URL can:
- Improve click-through rates: Descriptive and readable URLs attracts up to 25% more clicks.
- Improve rankings: Including relevant keywords in URLs can help you achieve higher rankings.
- Improve user experience: Users prefer URLs that are easy to read and remember.
- Improve crawling and indexing: Clear and simple URLs make it easier for search engine crawlers to crawl and index your page.
User-friendly UX
A user-friendly UX is an interface design that is intuitive, easy to navigate, and meets the needs of the user. It focuses on providing enjoyable experience, reducing friction and frustration for users.
Key principles include simplicity, consistency, accessibility, and responsiveness.
Google emphasizes the importance of user experience as a crucial factor in SEO. A positive UX leads to better engagement, higher retention, and improved satisfaction, which in turn can enhance a site’s SEO performance.
Google uses metrics such as page load time, mobile-friendliness, and ease of navigation as part of its ranking algorithms.
What to consider when creating landing pages UX?
- Mobile-first design: Google runs on a mobile-first indexing hence you need to create landing pages to fit mobile devices and fit to desktop. Google will evaluate your mobile version.
- Clear and simple navigation: Make it easy for users to find the information they need quickly and without putting in effort or finding their inner detective.
- Fast load times: Optimize images and scripts to have landing page load fast, as slow load times can frustrate users and increase bounce rates. Avoid using unnecessary website plugins.
- Compelling content and CTAs: Provide relevant content and clear calls-to-action that guide users towards the desired action.
- Accessibility: Make sure your landing page is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. This includes using alt text for images, easy keyboard navigation, and providing sufficient contrast in colors on images, background, buttons, links, etc.
- Consistency in design: Use consistent fonts, colors, and styles to create a cohesive look and feel that users can easily understand and navigate.
So, user-friendly pages are good for your on page SEO efforts.
But this is not the only thing about optimizing user experience.
User-friendly webpages increases business because of:
- Increased conversion rates: Well-designed landing pages with clear CTAs can lead to higher conversion rates, as users gets simple directions and shown the way to the desired action.
- Improved rankings: Google rewards websites that provide a good user experience by ranking them higher in search results.
- Better user retention: A positive UX encourages repeat visits and improves user loyalty, contributing to long-term customers.
A useful On Page SEO checklist

Follow my on page SEO checklist to achieve successful SEO:
- Page is target for one main keyword or topic
- You have searched the keyword on Google and determined search intent
- You have checked for broken links
- The page is passing the Page Speed Test
- External links opens in a new tab
- Header hierarchy is logical and answers the next logical question
- Keep URLs short, clear, and use hyphens to separate words.
- Start page titles with your keyword, include a CTA, and keep it under 70 characters.
- Craft engaging meta descriptions under 160 characters to attract users.
- Include your main keyword in the H1 heading.
- Ensure your main keyword appears in 60-70% of H2 headings.
- Use related keywords to add context and aid search engines.
- Link internally to boost important pages.
- Place your keyword within the first 100 words (above the fold).
- Aim for at least 1,000 relevant words (or 2,000 for blog posts).
- Double-check grammar; it’s a ranking factor. Use tools if needed.
- Use different keyword variations for image alt-tags.
- Rename images with relevant names.
- Compress images with tools like TinyPNG.
- Use great images and videos to boost time spent on page.
- Create engaging, original, and helpful content to retain readers. Provide value.
- Link out to relevant and authoritative sites.
- Optimize for conversions. Make it easy for users to take action.
- Use a reliable caching service.
Advanced On Page SEO
As you dig deeper into SEO, it’s crucial to explore more advanced On Page SEO techniques that can increase your rankings further.
Beyond the basics, advanced strategies focus on creating a more structured, user-friendly, and search-engine-friendly site.
In this section, we’ll cover three key areas: Topic clustering, Schema markup, and optimizing for Featured Snippets.
These methods will help you organize your content more effectively, boost the appearance of your site in search results, and improve your chances of being highlighted by Google.
Topic Clustering
Topic clustering is an advanced SEO strategy that is about organizing your content into clusters around a central theme, known as the pillar page.
The pillar page covers a broad topic in depth and links to cluster content, which covers subtopics related to the main theme.
This approach not only helps search engines understand the structure and relevance of your content but also increasing user experience by providing comprehensive coverage of a subject.
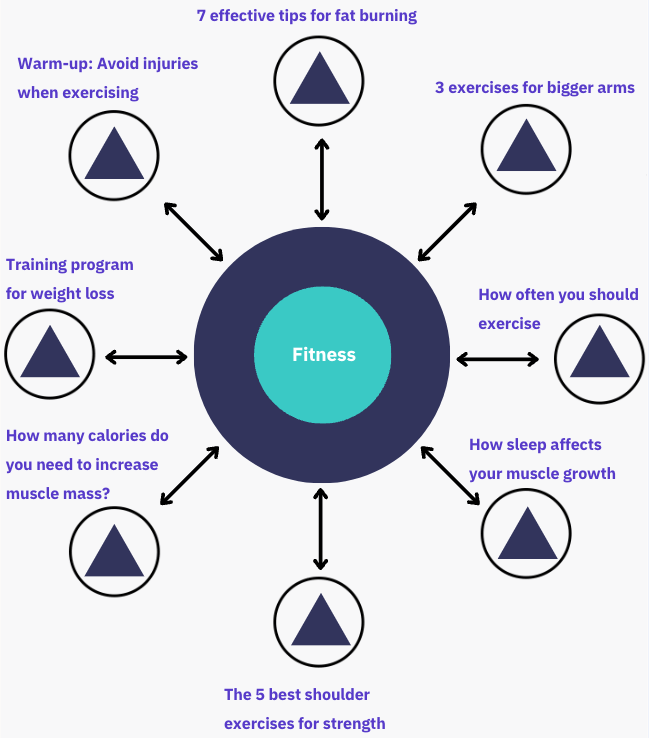
Benefits of topic clustering
- Improved rankings: By creating interlinked clusters of content, you signal to search engines that your site is an authority on the subject, which can improve your rankings.
- Better user experience: Users find it easier to navigate and find the information they need when content is well-organized. Let’s call it a one-stop-shop.
- Increased dwell time: Linking to related subtopics encourages users to stay on your site longer, reducing bounce rates and increasing engagement and so called long clicks which is also a ranking factor.
How to create topic clusters
- Identify pillar topics: Choose broad topics that are central to your business and have significant search volume.
- Develop cluster content: Write detailed articles on subtopics related to your pillar topics. Remember each piece of cluster content links back to the pillar page.
- Interlink strategically: Use internal links to connect your pillar page with its cluster content, creating a web of related articles that search engines can easily crawl and index. Google will reward you for having all relevant info on a topic in depth.
Apply Schema
Schema markup is a form of microdata that you can add to your website’s HTML to help search engines understand, interpret and display your page in search results.
Implementing schema can help your site achieve rich snippets, which are more attractive to users and can improve your click-through rates.
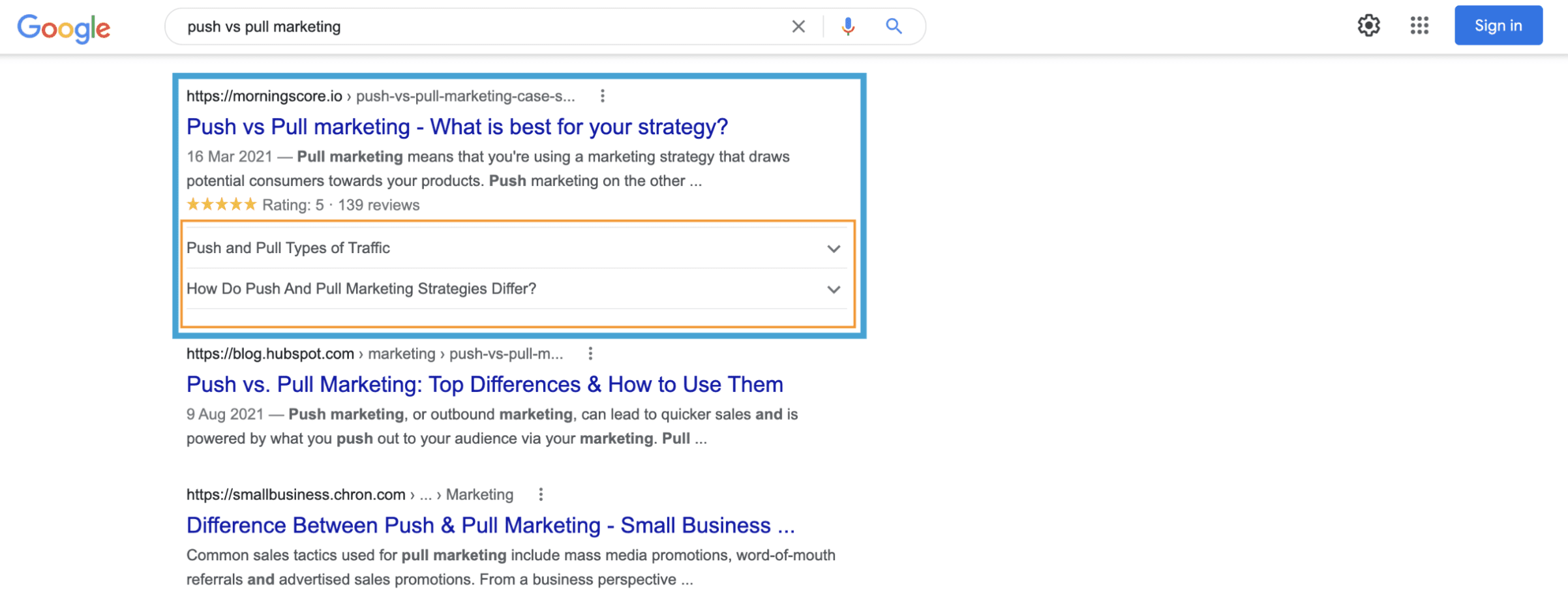
Benefits of Schema markup
- More SERP visibility: Schema markup can add elements like star ratings, images, and other information to your search results, making them more attracting and outstanding.
- Improved click-through rates: Rich snippets stand out in search results, which can increase your organic traffic.
- Better context for search engines: Schema provides additional context about your content, helping search engines understand its relevance and purpose.
How to Apply Schema Markup
- Choose the Right Schema Types: Identify which types of schema markup are most relevant to your content (e.g., Article, Product, FAQ, Recipe).
- Add Schema to Your HTML: Use schema.org guidelines to add the appropriate microdata to your HTML code. This can be done manually or using plugins if you’re using a CMS like WordPress.
- Test Your Markup: Use Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to ensure your schema is correctly implemented and will be read by search engines.
Optimize for featured snippets
Featured snippets are selected search results that appear at the top of Google’s search results, providing quick answers to users’ queries.
Optimizing your content to be featured in these snippets can significantly increase your visibility and drive more traffic to your site.
Achieving featured snippets are the shortcut to the top of the search results. Often, you need to rank within top 10 (page 1) to achieve it though.
Types of featured snippets
- Paragraph snippets: Typically provide definitions or answers to questions.
- List snippets: Can be ordered (step-by-step instructions) or unordered (bullet points).
- Table snippets: Display data in a table format.
How to optimize for featured snippets
- Identify common questions: Use tools like Answer the Public and keyword research tools to find common questions related to your topic. Answer objectively, short and precise.
- Provide clear and concise answers: Write short, direct answers to these questions within your content. Aim to answer the question within the first 100 words without any fluff.
- Use proper formatting: Format your content to match the type of snippet you’re targeting. Use bullet points for list snippets, clear paragraphs for paragraph snippets, and tables for table snippets. For paragraphs you can make the answer to the question bold.
- Optimize headers: Use question-based headers (for example “What is On Page SEO?”) to align with user search queries.
- Add structured data: Applying schema markup can also help search engines understand your content better and increase your chances of being featured.
On Page SEO FAQ
Why is On Page SEO important?
On Page SEO is not only important to achieve more visibility in SERP and rank higher on more relevant keywords. On Page SEO is about creating the best possible user experience for your audience.
What are the key elements of On Page SEO?
Key elements is title tags, headers, URL structure, internal linking, and content optimization. Every single thing is important and will boost your rankings so don’t prioritize these elements only. Nothing can stand alone in SEO.
How do title tags impact SEO?
Title tags tell search engines what your page is about and are a major factor in determining your ranking.
What makes a good meta description?
A good meta description is concise, compelling, includes relevant keywords, and accurately summarize the page content.
What is the role of internal linking?
Internal linking helps distribute page authority and ranking power across your site, improving navigation and SEO.
What is keyword density?
Keyword density is the percentage of times a keyword appears in your content relative to the total word count. Mentioning a keyword 3 times in a 100 word blog post results in a keyword density of 3%. Google don’t pay attention to keyword density, but you should check that it’s not 10% and stuffed with keyword for no reason.
How does mobile optimization affect On Page SEO?
Mobile optimization makes sure that your site is user-friendly on all types of devices, which is important as Google prioritizes mobile-first indexing.
What is the importance of page speed in SEO?
Faster page load times improve user experience and are a ranking factor for search engines.
How can I improve page speed?
Optimize images, use browser caching, minimize CSS and JavaScript, and leverage a content delivery network (CDN).
How does content freshness impact SEO?
Regularly updating content signals to search engines that your site is relevant and up-to-date, which can improve rankings.
What are alt tags and why are they important?
Alt tags describe images to search engines, improving image SEO and accessibility for users with visual impairments. This is not necessarily important for your website if your audience don’t do image search for your products.
How can I optimize my images for SEO?
Use descriptive file names, add alt tags, compress images to improve load times, and choose the right file format.
How does bounce rate affect SEO?
A high bounce rate may indicate poor user experience, which can negatively impact your rankings. People visiting your website and then exit to visit another one shows search engines that you either provide low quality content, don’t match the users search intent or have over-promised what users can expect of your page.

