Sometimes you just get stuck on questions like:
- Should I rank for “.. service” or “.. services“?
- Does Google see them as synonyms?
- Are they both as popular? Or is there any difference?
- And will I rank for both versions if I optimize around only one of them?
Normally, for such dilemmas, you’d simply fire up your keyword management tool of choice and decide.
But this particular one can be tricky. That’s because, unfortunately, no SEO tool can give you the answers for such questions.
Instead, you need to make the right decision. So I’ll show you just that – how to decide whether to target the singular or plural form of your main keyword.
Things can seem complex at first, but I promise you that it’s easier than you might think. Without further ado, let’s dive right into yet another captivating Search Engine Optimization question.
Which Keyword Phrase To Use – Singular Or Plural?
The short answer is that if both the singular and plural versions of your keyword have the same amount of Search Volume, optimize for the plural form since the singular form will be included in it by default. But remember that things aren’t always black and white – and therefore you always need to use your judgment.
However, there are a few variables that you need to think about before truthfully answering this question.
- Firstly, you need to make sure that the Search Intent (aka User Intent) behind both of the search queries matches (more on this in the next section).
- If the keyword searches match and there is no difference in the search results, next check up on which keyword actually gets more monthly searches (i.e. based on Search Volume). If there are big differences, go for the keyword with more Search Volume.
Now, as promised, let me show you how you can check whether the Search Intent between your target keywords matches.
How To Check If Singular Or Plural Keyword Is More Relevant?
To check if you should use the singular or plural version of your keywords, you need to do what we like to call a “SERP Similarity Analysis” (explained below). With it you can check how similar the search results are for a few different keywords. If they overlap, you can safely use either one or the other. If there’s a large difference in the search results, however, with this analysis you can determine which the right variation is.
But checking the SERPs for whether Google prefers singular or plural keywords for your target phrases can be a bit tricky if you’re not using a keyword research tool. That is because even in incognito Mode, your browser and internet provider still give Google enough data to customize the search results. Therefore, it’s hard to determine the truth by looking at such biased data. Additionally, you can no longer simply change your default Google search location and expect the results to adjust.
Because of that, to see as neutral results as possible, you’ll need to use an SEO tool. And in particular, one that specifically allows you to check the SERP for your given keywords. In fact, the good thing here is that you can apply this technique to not only singular and plural search terms but also to analyze more broad, different search results. So here’s how you can do exactly that in Morningscore:
1. Add the singular and plural variations of your target keywords to the Rank Tracker.
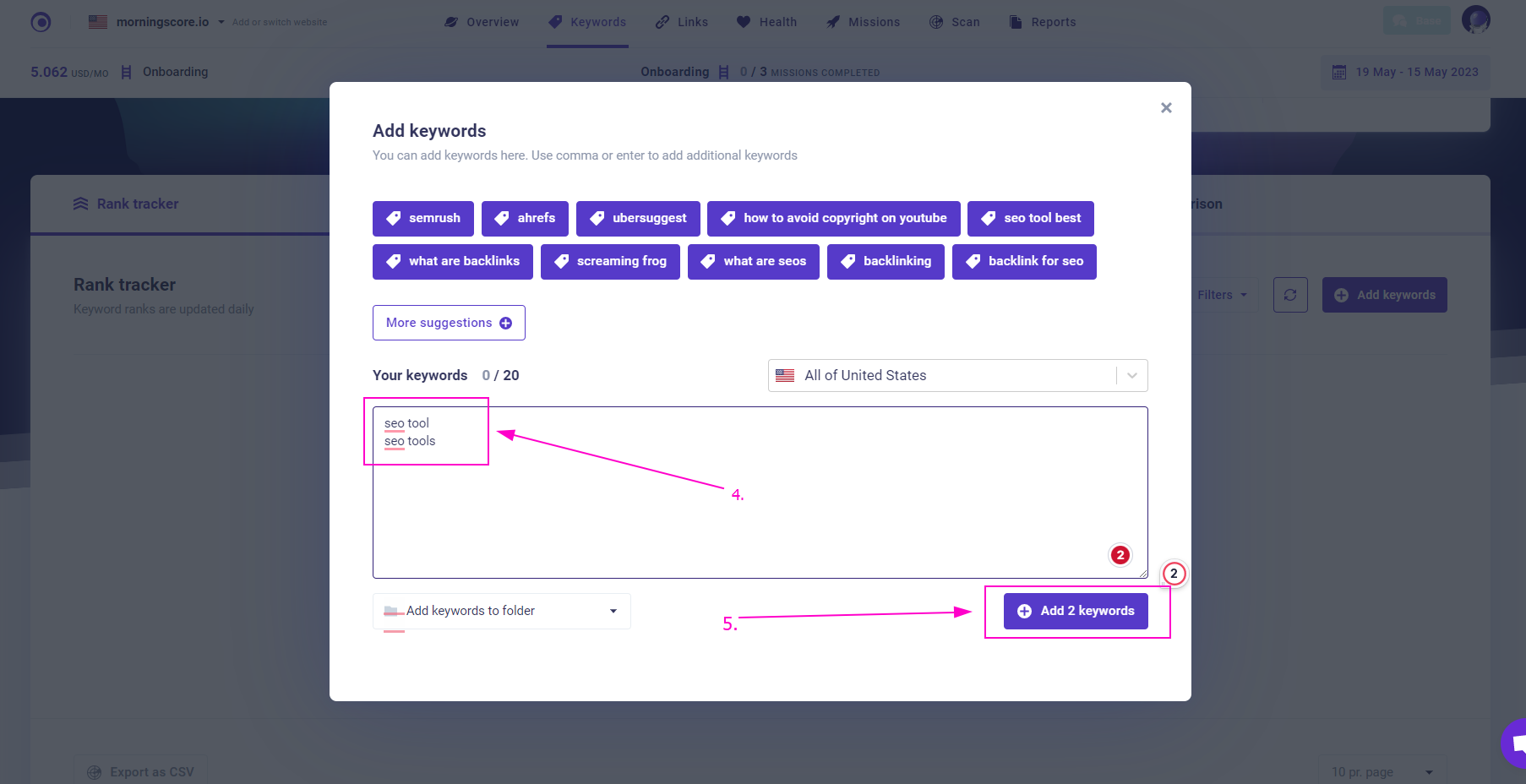
2. Right-click on either of them and in the contextual menu select “See All Ranks”.
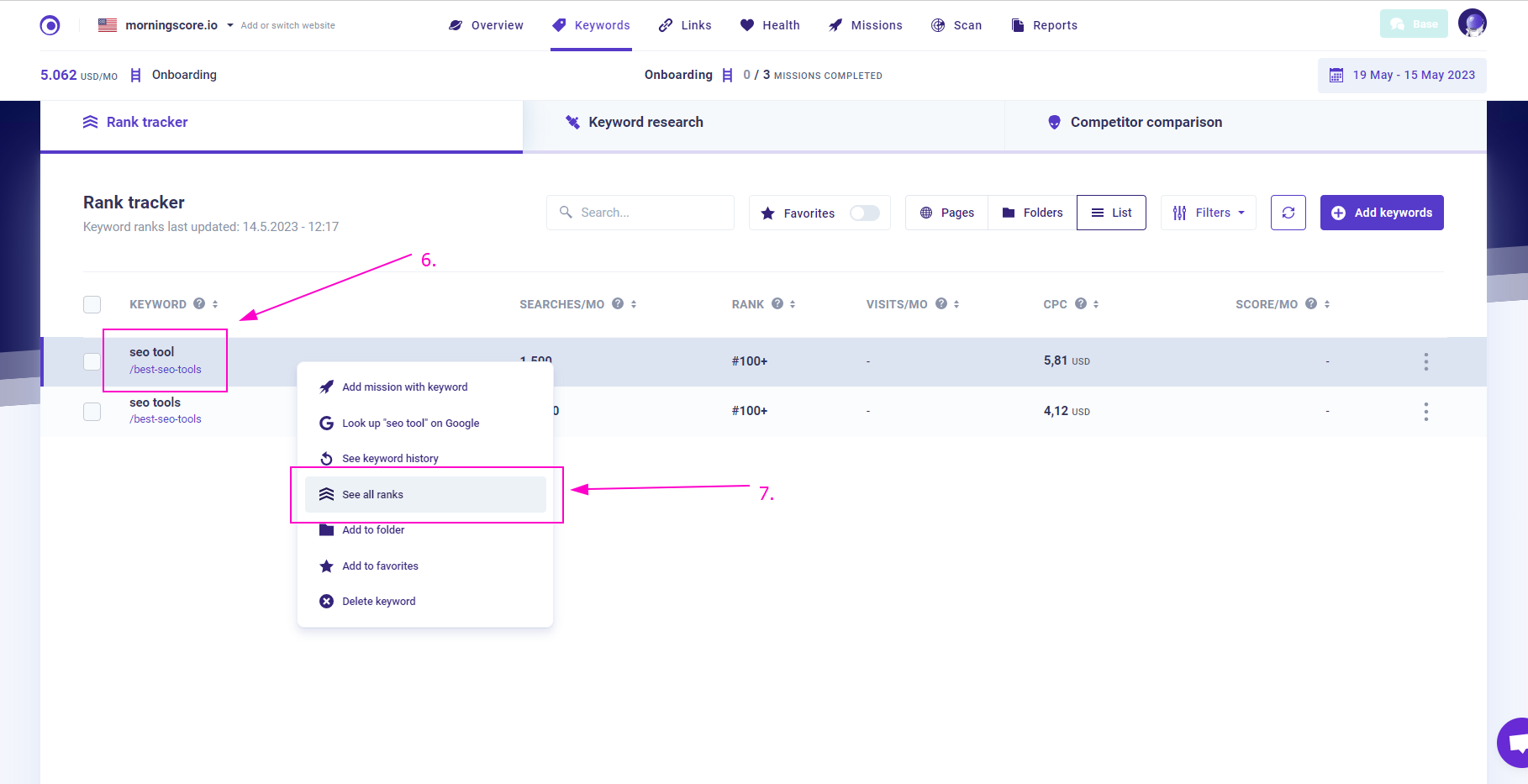
3. In the new window, you will see an unbiased list of the top results.
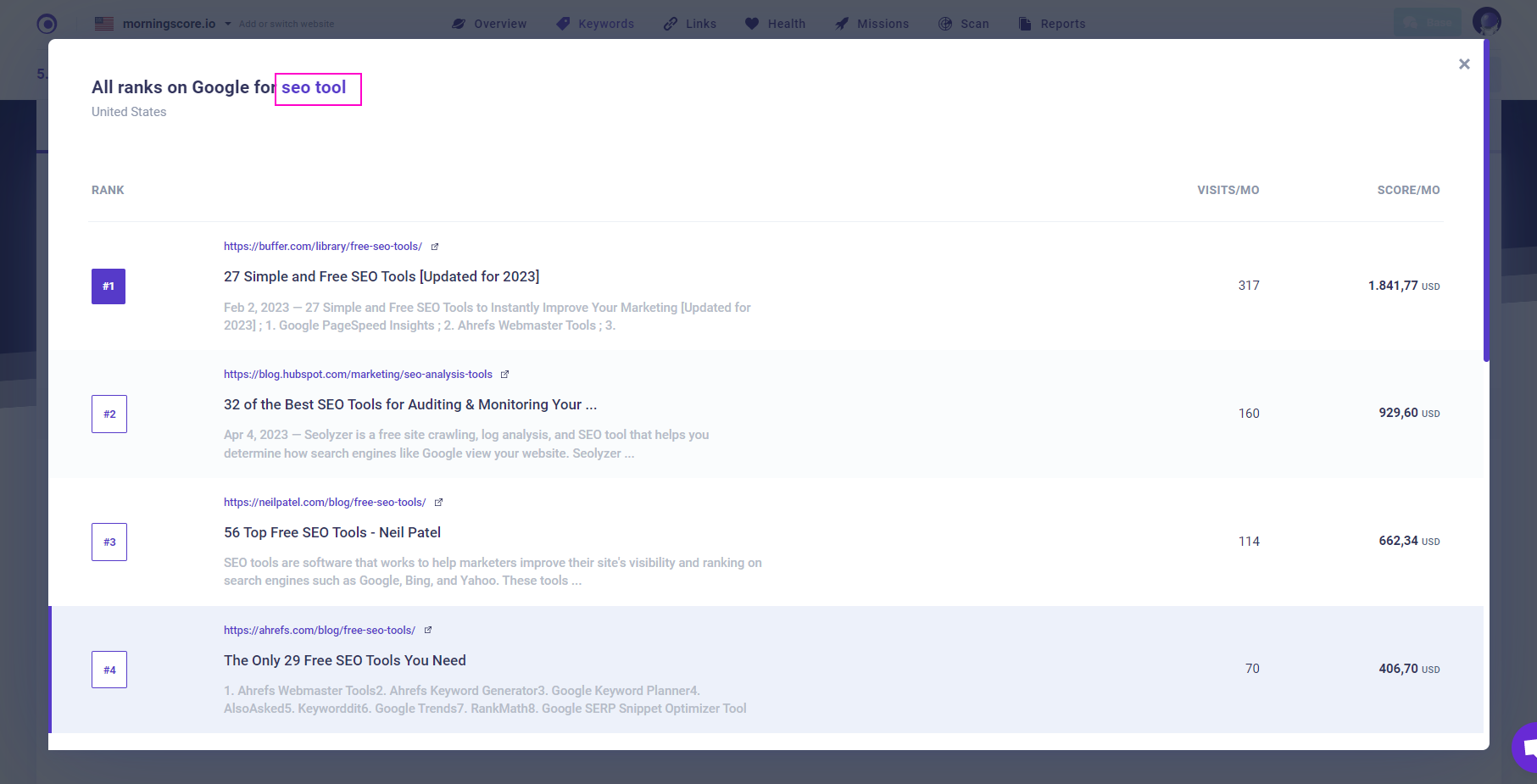
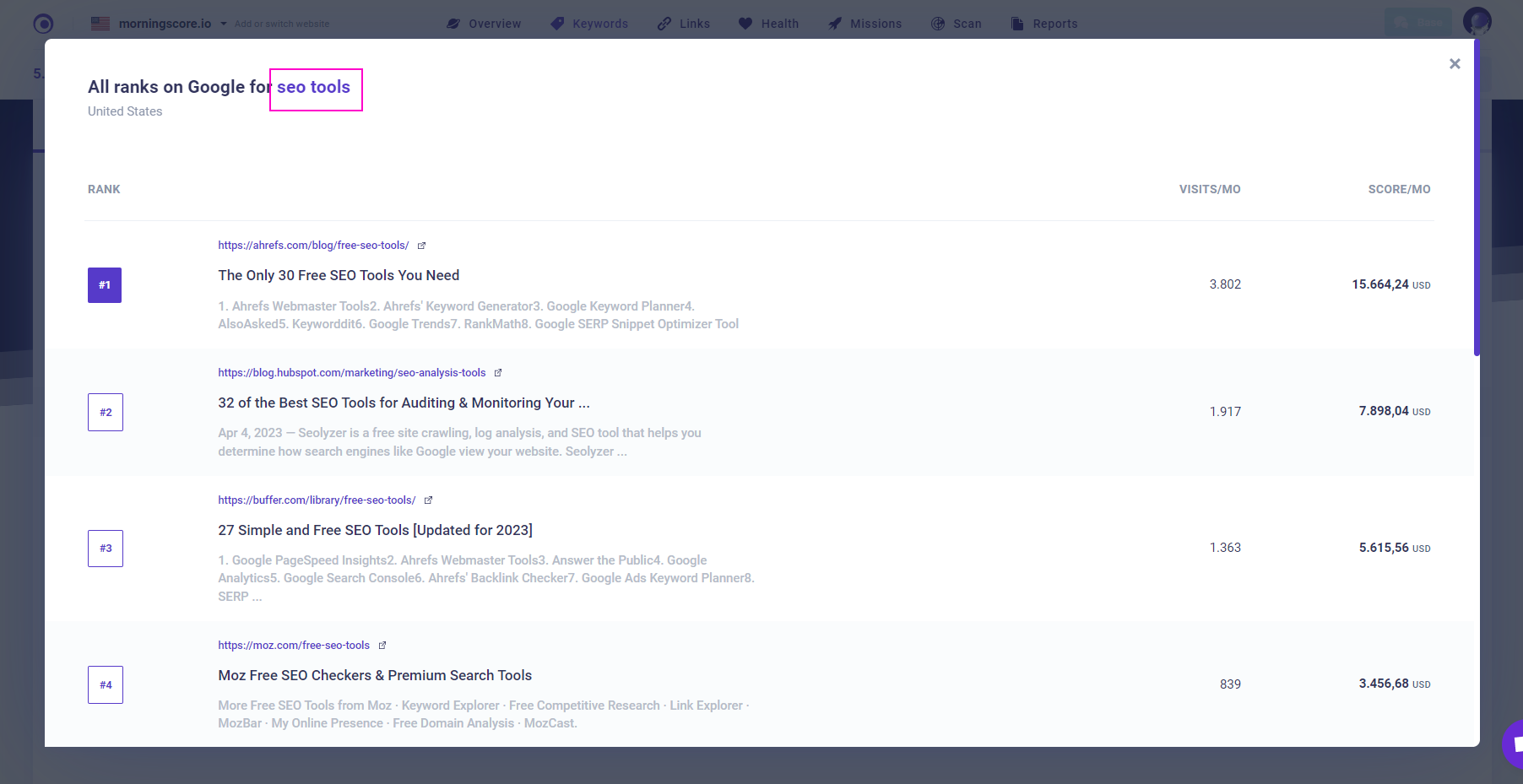
Now, there are 2 things to look out for here:
- Straight off the bat, you can see whether the preferred choice for your products is in singular or plural form
Sometimes, this will be clear right away. That is important because it gives you an informed guess on what the users expect and prefer to see when they open the website. If the websites ranking at the top use the singular form of the word, then go for that. Alternatively, if the top ranking websites use the plural version, go for that instead.
And in the cases where you can’t really determine it from the result page, simply open the top 3 sites and inspect the content on their pages. If the singular form is present in the headings and in the text, and the plural form appears way less often, then go for that. If that’s the case and you can’t really tell which you should target it’s safe to assume Google sees no major differences between the two keywords. Simply target the one that has more Search Volume.
- Additionally, you can also see whether the search results actually differ for each of your keywords
Why is that important? Because sometimes Google ranks different pages for the singular vs plural form of the words. This usually happens when there is different Search Intent behind those keywords, and can sometimes indicate whether one of the phrases has a different meaning than its counterpart.
Can You Determine The Search Volume Using Google Keyword Planner?
Now, it’s important to also differentiate between the different results in search terms for SEO and Google Ads.
There’s a lot of information available on how Google handles specific keywords in their Keyword Planner Tool. Because of that, it’s important to make the distinction between the different match types.
They affect the data that you see in Google Ads directly, and are strongly related to how many other advertisers there are.
For example, Exact Match, Broad Match, and Phrase Match are different types of keywords in the Google Ads platform and do not represent the final picture when it comes to SEO.
In Google Ads, you’re unfortunately often unable to do accurate keyword research. That’s because the platform groups plural and singular terms and you can’t easily determine which one has a higher search volume.
All of this means that it is not the best decision to rely on that data when trying to determine which keyword to optimize for in your keyword strategy.
Now, this might have spiked some curiosity in you. Because of that, let’s explore why singular and plural keywords can actually rank differently in Google.
Why Do Singular And Plural Keywords Rank Differently?
The reason for why singular and plural keywords can rank differently in Google is that everything is based on Search Intent and User Signals. Based on these two factors, Google can determine whether or not the user expects a different set of results for each of the keywords.
Sometimes the singular and plural forms of phrases can mean different things. Or at least, they can indicate that the user has something else in mind than what’s expected. And that can lead to Google displaying different search results. Now, the different results might be simply based on semantics – or they could be totally different based on the different user intent.
For example, someone searching for “car dealers” can expect to see a list of car dealership locations in their area. On the other hand, someone searching for “car dealer” could be expecting to see the video game on Steam called Car Dealer or simply trying to understand how car dealerships work.
In those cases, your rankings can be different for the keywords – and you should therefore aim to use the right phrase for the right target audience.
If you are a car dealership trying to sell cars to consumers, from the example above, you need to target “car dealers”. On the other hand, if you’re one of the team members of the piratecat games publisher (Hi, there!) who wants their Car Dealer game to rank high in the search results, you need to target “car dealer” as your target keyword (which non-coincidentally is also your game’s brand name keyword).
There’s Always An Exception To The Rule
While there are many exceptions to the rule, I’ve noticed that differences in search results for singular and plural forms usually occur when we’re looking at broad “defining” terms (i.e. definitions) for topics and subjects (e.g. “affiliate marketing”). Usually when people search for such topics, it’s hard to determine exactly what they are looking for (i.e. determine the User Intent) simply because it’s so broad.
For example, are they looking for a to-the-point definition of the term? Are they browsing for some sort of guide or a course? Some interesting case study or research to use as a source in their papers? We’ll never know.. 🙃
Bottom line is, if you rank well for one of the keyword forms but very far down for the other form, there’s likely a good reason for it that’s rooted in the differences between user intent – and that’s actually best for you because you wouldn’t want that irrelevant traffic anyway which can hurt your overall conversion rate.
Now, let’s see how you can optimize your pages for when you want to rank for both of the keywords.
Should You Create Different Pages For Your Singular And Plural Keywords?
The quick answer is no. If the Search Results overlap for both the singular and plural keywords, you should never create more than one page targeting each form. This can cause serious duplicate content and keyword cannibalization issues. It can also confuse both Google and your end users.
For example, if you’re a grocery store that wants to rank for both the keywords “grocery store” and “grocery stores”, do not create two pages targeting both of these keywords as it will hurt your rankings. Google sees no difference between the plural and singular search for your related keywords.
The only instance where you should consider creating different unique pages for both the singular and plural keywords is if the Search Intent behind them is different AND you offer both of the “solutions” (i.e. products, services, etc.) for the search.
But the only example I could think of is likely Amazon so that might not really apply to you (otherwise, Hi Amazon!). Because they have so many different product variations, it is likely that they have dealt with this issue before.
As per the example we gave just above, if (for some reason) you are both a car dealership AND offer the Car Dealer game available on Steam, it is perfectly reasonable to create two different pages. But keep in mind this example is not limited to any industry. In fact, you can experience this for anything from e-commerce sites to blog posts.
But worry not, as for the vast majority of companies this never happens and doesn’t require a dedicated SEO strategy to handle.
How To Optimize For Both Plural And Singular Keywords?
When optimizing for both the singular and plural versions of your target keywords, you need to ensure your texts don’t sound spammy and awkward. Do not create two different pages for each word variation – as this is a bad, outdated tactic both in Google’s and the end-users eyes.
The first thing that comes to mind for many (especially beginner SEOs) is to simply use both versions throughout your text. And this is fine as long as you monitor your overall keyword density. However, there are more creative ways to get around using both versions in your important elements like your Title Tags, H-tags, and Meta Descriptions. Let’s look at some examples of how you can do that.
In Titles:
The best way to feature both the plural and singular versions of your keywords is to use them in combination with your Unique Sales Points & Unique Value Proposition as a sentence. Here are 3 concrete examples of how you can do that the wrong and right ways:
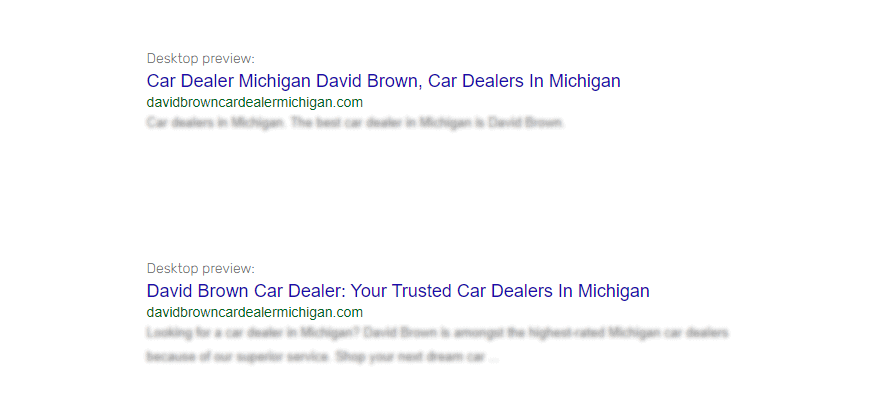
Examples of Title Tags for “Car Dealer” & “Car Dealers”:
- ❌ Car Dealer Michigan David Brown, Car Dealers In Michigan
- ✅ David Brown Car Dealer: Your Trusted Car Dealers In Michigan
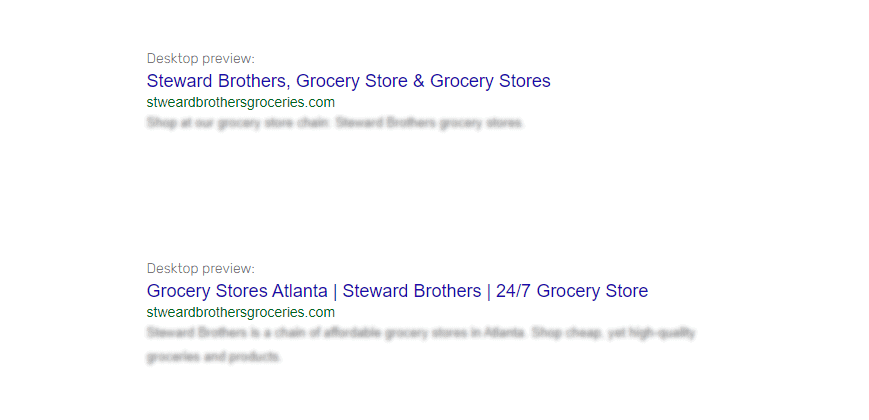
Examples of Title Tags for “Grocery Store” & “Grocery Stores”:
- ❌ Steward Brothers, Grocery Store & Grocery Stores
- ✅ Grocery Stores Atlanta | Steward Brothers | 24/7 Grocery Store
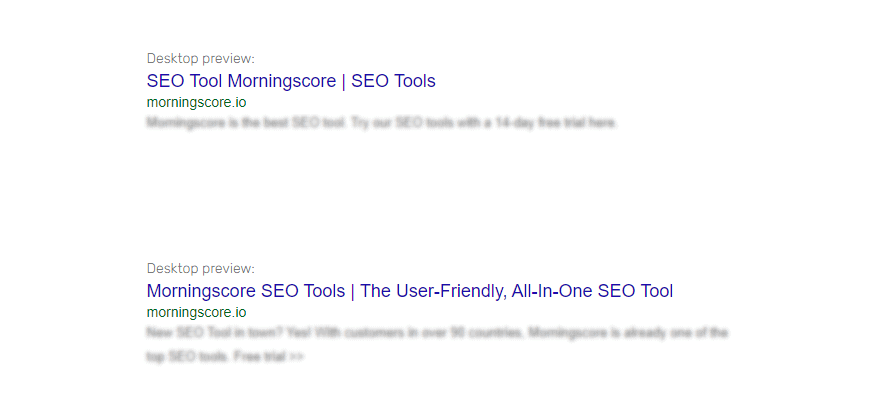
Examples of Title Tags for “SEO Tool” & “SEO Tools”:
- ❌ SEO Tool Morningscore | SEO Tools
- ✅ Morningscore SEO Tools | The User-Friendly, All-In-One SEO Tool
As you can see in the examples above, it’s also important to have your primary target keyword as close to the beginning as possible. Once again, this factor serves both Google (and other search engines) and the end user.
In Meta Descriptions:
The easiest way to feature both versions of your keywords in your Meta Description is to use one of them in a question and the other in the answer. Also, once again, remember that to combine them with your USPs & UVPs because that can be the difference between the user clicking or not. Here are some examples:
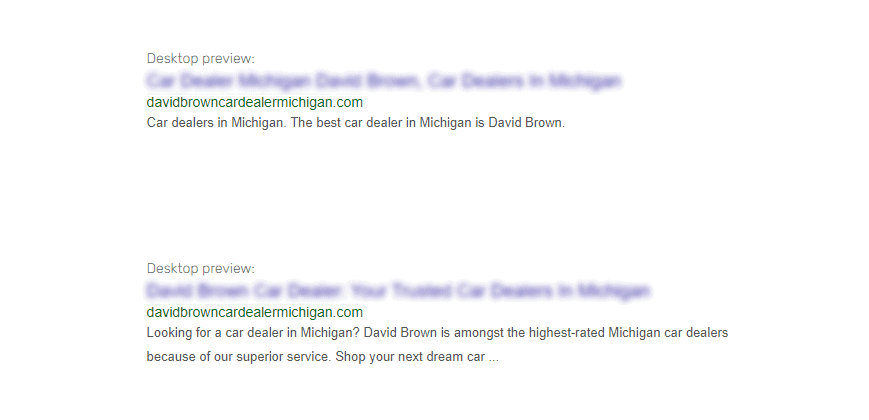
Examples of Meta Descriptions for “Car Dealer” & “Car Dealers”:
- ❌ Car dealers in Michigan. The best car dealer in Michigan is David Brown.
- ✅ Looking for a car dealer in Michigan? David Brown is amongst the highest-rated Michigan car dealers because of our superior service. Shop your next dream car.
Examples of Meta Descriptions for “Grocery Store” & “Grocery Stores”:
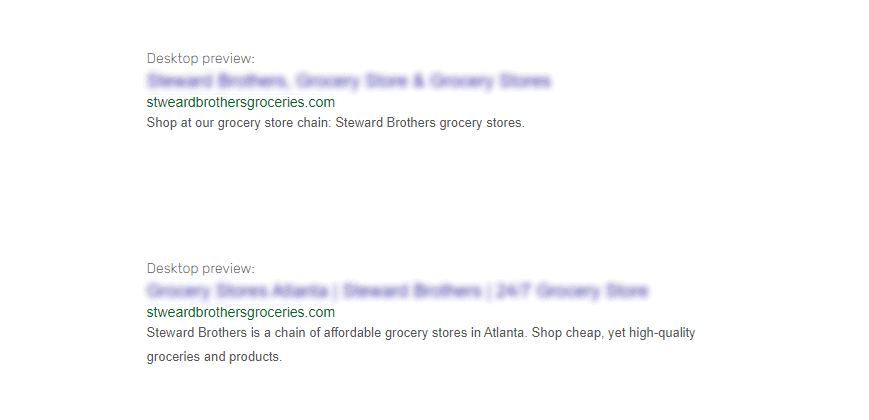
- ❌ Shop at our grocery store chain: Steward Brothers grocery stores.
- ✅ Steward Brothers is a chain of affordable grocery stores in Atlanta. Shop cheap, yet high-quality groceries and products.
Examples of Meta Descriptions for “SEO Tool” & “SEO Tools”:
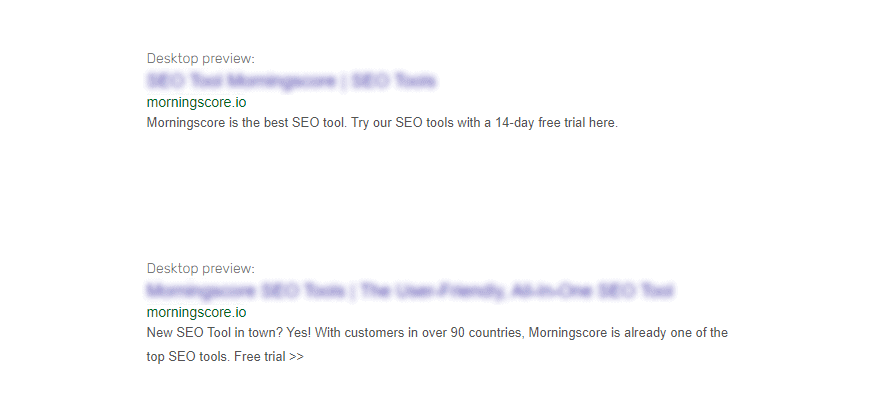
- ❌ Morningscore is the best SEO tool. Try our SEO tools with a 14-day free trial here.
- ✅ New SEO Tool in town? Yes! With customers in over 90 countries, Morningscore is already one of the top SEO tools. Free trial >>
Alternatively, you can opt in for using each unique form once throughout the different elements. That is, you can use the singular form of your keyword in the Title Tag and the plural form in the Meta Description. This will free up even more space for using UPSs which will further help you convince the end user they should click on your search result.
In Headings:
Firstly, the general rule of thumb is to use your target keyword in no more than 70% of your H-tags. With that, if you’re really targeting both keywords, simply alternate some of them in your Headings. For example:
❌ Example of Bad Headings for “Car Dealer” & “Car Dealers”:
H1 – Michigan Car Dealership, David Brown Car Dealers
H2 – David Brown Car Dealers
H3 – Car Dealer In Michigan David Brown
✅ Example of Good Headings for “Car Dealer” & “Car Dealers”:
H1 – David Brown: One Of The Highest-Rated Car Dealers In Michigan
H2 – Where To Find Our Car Dealer In Michigan?
H3 – New Vehicles In Every Thursday
❌ Example of Bad Headings for “Grocery Store” & “Grocery Stores”:
H1 – Best Grocery Stores
H2 – Great Chain Of Grocery Stores
H3 – Cheap Grocery Store In Atlanta
✅ Example of Good Headings for “Grocery Store” & “Grocery Stores”:
H1 – Steward Brothers: Atlanta’s Best Chain Of Grocery Stores
H2 – What Makes Our Grocery Store So Great?
H3 – Our Customers Say It Best
❌ Example of Bad Headings for “SEO Tool” & “SEO Tools”:
H1 – Morningscore SEO Tool
H2 – Best SEO Tools
H3 – SEO Tool With Accurate Data
✅ Example of Good Headings for “SEO Tool” & “SEO Tools”:
H1 – SEO Tools For Beginners & Pros Alike
H2 – You Don’t Have To Be A Pro To Get Started
H3 – Customers In Over 90 Countries Love Our SEO Tool
In Main Content:
This should come naturally. Simply use either of the versions throughout your main content. You can also use it as part of your Alt Tags.
Should You Edit Your Page If You Rank For One Of The Forms But Not The Other?
If you’ve put a lot of effort into ranking at the top for the singular (e.g. “Michigan car dealer”) but later find out that Google prefers (e.g. through Google Autocomplete) the plural form (e.g. “Michigan car dealers”) of your keyword, there are a few things you can do:
- In the main body of the text, change some of the instances of the keyword to the plural version or add a bit of content containing the plural version of the keyword.
- In your Title Tag & Meta Description, if you’re using only 1 version of the word, change one of the instances.
As a side note, here are some extra tips to keep in mind if your page is not ranking for both the singular and plural versions AND there’s no obvious reason it shouldn’t. The general idea here is to make sure that the user experience is “congruent”. That is:
- Meta Descriptions should “speak” to the users and be as relevant as possible to their specific search. Following the example above, the search query “Michigan car dealer” should return a result whose description talks about a dealership in Michigan.
- Similarly, the content on the page the user ends up on once they click that result should be relevant to the term itself. Again from the example above, the page that the user opens should have consumer vehicles – and not, for example, images and listings of taxi cars.
What To Do If You’re Still Unsure?
If after reading all you can on the subject and still not knowing what to do, there’s a very simple way to solve the issue.
If you’ve already optimized your page for one of the variations, do this:
- Open your Google Search Console.
- Inspect the keywords you already rank for.
- Here you need to check how many impressions and clicks you get for what keywords. The keyword with the most impressions (and potentially the most clicks) is the one you should target.
- If that’s the one you’re already targeting, focus on improving other things and don’t worry about it.
- And if it turns out to be the other variation, simply edit your page with the tips shown above.
However, if you haven’t yet optimized the page and are still in the planning stage, simply pick the one you feel most comfortable with. From there, repeat the process above once you get sufficient Google Search Console data (at least 1-3 months).

